Albert Lasker in the middle of the last century, when there was already radio and television, called advertising "the art of selling through the printed word." It has previously been noted that print advertising is an older form of advertising than print advertising. This is historically the first form of mass advertising, the main advantages of which include its availability for almost all levels of business, as well as the fact that most people belong to the category of so-called visuals (as opposed to "audials" and "kinesthetics"), i.e. people for whom the visual perception of information provides the best opportunities for its assimilation.
What unites print advertising and press advertising is the identity of the media (paper or its substitutes), the nature of its perception (through visual perception and reading), as well as their less intrusiveness compared to audiovisual, radio or television advertising. However, their main difference is that print advertising does not belong to the media, as some researchers sometimes mistakenly believe, does not have such mass distribution channels as newspapers and magazines, and therefore, as a rule, is focused on narrower consumer groups.
To assess the feasibility of using print advertising, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of the reading audience and the target group, knowledge of the main goals of the Republic of Kazakhstan, the subject of advertising, regions of distribution, circulation, labor intensity and financial capabilities of the advertiser and, of course, the area of its preferred use. certain types. The study of advertising allows you to outline general recommendations to solve these problems. At the research stage, it is advisable to get acquainted with the main content of printed products of other companies, try to evaluate its advantages and disadvantages, and creatively transform the main ideas to create your own original solutions.
It must be remembered that for all forms and types of advertising without exception, copying and directly borrowing someone else's "advertising products" often plays into the hands of a competitor, and repeating someone else's mistakes is even more unforgivable. The next step after choosing a certain type of advertising and the formation of general ideas for its creation is drawing up its approximate, but rather detailed plan. In this regard, you should try to clearly articulate the benefits you advertise (from the purchase, the conclusion of the transaction, from the cooperation) in a restrained and understandable form. Before starting work on a document, you need to select a set of drawings, diagrams, graphs, the most important specifications and other necessary applications that may testify in favor of the advertised product (goods, services). Let's dwell on specific types of print advertising:
Informational (advertising) letter executed on letterhead and addressed to a specific person. Contains information about your company, its main activities (about the most important goods, services, etc.) and the goals pursued by writing this letter, i.e. actions that you can expect from the recipient. You can offer the addressee to sell goods, provide a specific service, inform about price reductions, discounts, new partners, branches located near the addressee, offer cooperation, etc. The letter can be individual and typical (the text is addressed to several recipients, and the name of each is printed at the top of the letter indicating the position, surname, initials, etc.).
Commercial offer- advertising material, which has a lesser advertising focus and more commercial information content. Usually sent to a correspondent who is familiar with your company through some previous contacts. Contains a detailed description of your proposals and their active argumentation. In the appendix to the commercial offer, materials describing the object of the offer may be given: calculations, drawings, photographs, diagrams. From ordinary letters Commercial offer differs in the care of execution, the best design. Sometimes they are prepared in advance and transferred (sent) as contact with the intended partner is made (at exhibitions, business meetings).
Information sheet- similar information letter, but does not contain the attributes of the destination. Letterheads for writing it are usually not used. Brand name, logo and corporate colors can be used as design elements. Includes data on prices, discounts, benefits, etc. Since the information sheet is not addressed to a specific person, but to persons who are only supposedly interested in your offer, the presentation of the essence is simplified, but the main characteristics and comparison with analogues are presented quite fully.
Flyer (leaflet)- a simple unfolded promotional material containing purely promotional information about a product or a small group of them. It is brightly designed, has a pronounced advertising text. The American version is the dodger. Often, when designing it, they resort to funny, funny drawings, place an advertising slogan on it. Its main function is to be noticeable, to catch the eye. A flyer is similar to a press release, but at a lower cost it can be much larger and describe the subject of the advertisement in more detail.
Booklet- well-designed promotional material about a company or a specific product (service) or a group of them. Small in volume, often A4 format with a 6-page fold. To a greater extent, it refers to advertising materials of a prestigious orientation, often issued by firms that have achieved certain successes, or on anniversaries.
Flyer. Just like the booklet, it is more related to promotional materials of a prestigious, image character. More voluminous than a booklet (most often there are 10 or more pages), contains many color photographs and drawings. Often issued for a new type of product or for anniversaries. Sometimes it contains information of an economic, financial nature, photographs of company executives. Prospectuses can be commodity, tourist, trade, etc. A special type of advertising brochure is folder- the simplest and cheapest type of advertising brochure, intended for mass distribution. It usually consists of one sheet, sometimes folded in half, with short text, simple illustrations and graphics. In the form of a prospectus, annual reports, balance sheets of a company (bank) are sometimes drawn up. It is believed that booklets and brochures are either made of very high quality or not released at all.
Promotion Brochure- is an extended prospectus of 20 or more pages with more detailed information about the characteristics of the product. RB is sent or given to encourage participants in advertising contests, at exhibitions, applied to purchases, newspapers, magazines.
Catalog- printed, most often bound advertising material in the form of a booklet or magazine with a list of goods and services, their description, illustrated with photographs. Often beautifully printed, easy to use. The catalog does not always indicate the prices of goods due to the fact that it can be calculated for a long period of use, during which they may change. Hundreds of thousands of firms around the world conduct their catalog trade, sending out billions of catalogs every year. Catalogs of trade and manufacturing firms, exhibitions are a kind of regular catalogue. The so-called address directories are information printed edition, which contains complete lists of organizations, enterprises, firms of any industry (a number of industries) in a particular region or throughout the country. They are used in the organization of direct mail advertising.
The catalog may be intended for consumers, trade and other organizations. It may be widely used in the mail order business or be purely informational or technical in nature.
There are well-known "smelling" catalogs of perfumes, "playing" catalogs (of musical works, notes, etc.).
Press release- promotional material, to a greater extent focused on the press. Distributed at exhibitions, presentations, sometimes sent to the editors. Contains information about the success of the company, the most famous types of products, charitable activities. the main objective publication of press releases - to promote the dissemination of information about the company, including through its "hit" on the pages of mass publications.
Poster (poster)- a kind of print advertising in the form of an ad of a fairly large format. The supposed homeland of the posters is China. Printed in Europe since the 15th century. The Frenchman Jules Cheret began printing colorful posters in 1850. They are classified into educational, political, propaganda, demonstration and trade. the main task advertising poster- draw attention to a particular product, service or event.
In the theory of the advertising business, it is believed that creating a good print ad is more difficult than advertising on television, where there are many assistants (lighting, action, music, optical effects, etc.). Print advertising, as a rule, can lead only one marketing motive, which consists in the product. Here you need to come up with a convincing, interesting headline, an advertising preamble, you need to hone each phrase so that it is aimed at a single goal - to bring YOUR offer to the reader's mind. Very often, print advertising is the basis of television and less often - vice versa.
The main elements of print advertising are textual and artistic foundations. I would like to further dwell on the variety of possibilities of printed fonts. Even using a home computer, you can demonstrate quite a lot of options:
The font is chosen based on many considerations: ease of visual perception, attractiveness, mystery, the general creative idea of the message, etc. The artistic design of print advertising, the use of photographs, drawings, color combinations, etc. is also of great importance.
Press advertising
Advertising in the press is one of the traditional, most common types of advertising in the media. Armand Deyan cites data showing that more than 50% of all advertising spending in France is spent on advertising in the press, this percentage is even higher in the Scandinavian countries. This is due to the availability of advertising in the press for the broad masses of the population, both in the material (cheapness of mass publications) and in the physical sense (can be read in transport, in the absence of electricity, etc.). Advertising in the press is considered unobtrusive, may have the nature of a document, and sometimes it is (“discount for the bearer of a newspaper clipping”), it is cheaper than radio and television advertising and convenient due to special editorial processing (for example, highlighting the headings “furniture”, “cars”, “household appliances”, etc.), popular due to the traditionally greater trust in the printed word. Advertising in the press, as already mentioned, is a significantly more massive type of advertising compared to print advertising, but also more expensive, since a large staff of workers - editors, designers, proofreaders, etc. is involved in its creation.
The situation with advertising in the press in Russia is different from most European countries and more similar (by rating) to the USA. In 2002, television ranked first in terms of advertising costs - about 900 million USD, the second - the press (about 600 million), and the third - outdoor advertising (400 million USD)2.
Advertisers most often resort to advertising in the press in cases where it becomes necessary to convey information about their company, its activities on the market, manufactured goods and their specific qualities, when it is necessary to find partners or sponsors for business cooperation among a fairly wide range of readers, and financial opportunities or considerations of expediency do not allow using the services of radio or television advertising. Thus, in all countries of the world (and even in the United States, leading in the field of television advertising), advertising of services tourism business predominantly published in newspapers and magazines. They also (mainly in expensive magazines) place advertisements designed for very narrow groups of consumers (for example, advertisements for expensive luxury car brands).
Press is a collection of periodic newspaper and magazine publications of an international, national, regional and local nature, covering both very large territories and masses of the reading population, and very small highly professional or political groups of up to tens of people. The periodicity of these publications varies from daily publication to one-time per year. When including advertising in the press among advertising activities, one must remember that most people are skeptical about advertising in general, but not about any advertising. The attitude of people to the press, in which the advertisement is printed, is transferred to this advertisement. If the publication is respected and trusted, then the advertising placed in it deserves more attention and trust and, thus, is more effective. Advertising in the press is quite heterogeneous in its composition and is classified according to a number of criteria.
- advertisements;
- advertising articles and other publications of an overview and promotional nature.
- commodity advertising;
- prestigious advertising.
- own preparation by the advertiser of the layout of the advertisement;
- use of services advertising agency or the media.
By geography of distribution:
- national editions;
- regional publications;
- local publications;
- transnational publications.
By target audience:
- socio-political;
- popular publications;
- specialized publications.
- information publications;
- advertising publications.
By frequency:
- daily publications;
- weekly publications;
- monthly publications.
By circulation:
- small circulation editions;
- multi-circulation editions.
Distribution method:
- by subscription;
- for free;
- retail.
There are certain features of newspaper and magazine advertising.
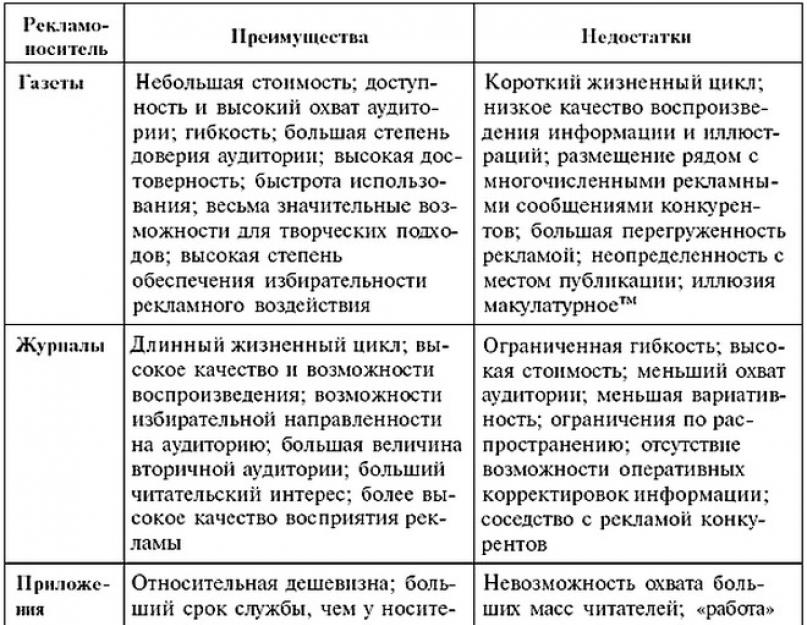
Newspapers have large circulations and lower cost, are more accessible to the general population. The advantages of newspapers include the fact that they display advertising of the most various levels, including advertisements for local retail services. Advertising messages can be placed with sufficient speed, coupon placement is widely used here, and some advertising items can be covered in detail, for which there is practically no time for radio and television advertising. Newspaper advertisements may include a map or plan showing how to find your business. Placing an ad in a newspaper is easier and cheaper than in other media. In addition, having made the original layout, it can be used repeatedly.
Among the shortcomings of newspaper advertising, one can note a short life cycle (approximately 24 hours) and insufficiently good quality of information reproduction, the predominance of black and white images. The quality of newsprint determines the fact that illustrations in newspapers are worse than photographs, which also affects the content and quality of advertising publications. Newspaper advertising often coexists with a mass of ads from other companies, which interferes with its perception. The modern reader spends less time reading newspapers, more often just skimming through them.
Prospects for the development of newspapers and newspaper advertising follow from the development of information and communication technologies. In particular, there is already a practice of transmitting newspaper information by fax (to subscribers who are away, to remote settlements, on ships), in real time on the Internet.
magazine advertising has a significant segmentation according to a large set of characteristics - income, demographic parameters, socio-educational and professional status, consumer interests, etc. The classification of journal periodicals includes consumer, business (trade, industrial, professional), farm, as well as magazines for women and children, educational institutions. Magazines can carry high-quality print ads in a wide range of colors for specialized audiences, and this level of specialization is increasing. The main disadvantages of journal periodicals are limited flexibility, high cost and certain difficulties in distribution. Prospects are connected with the development of virtual journal publications.
Advertising in the press now began to include advertising in various supplements to newspapers and magazines. In practice, advertisers usually use three types of applications: thematic, regional, electronic. The first are focused on the information content, the second - on the geography of distribution, the third - on the type of information carrier.
The most common type are thematic applications. They are issued on the basis of a magazine or newspaper periodically (once a week, a month, a quarter, etc.) or for special occasions (holidays, the opening of the season, etc.).
Ads in a themed app are generally more effective than in the pages of a magazine or newspaper. This is due to the fact that readers study the thematic application more carefully, store and use it for a long time. Depending on the type of application and the situation on the market, the duration of the effectiveness of advertising in it reaches up to a year.
Supplements are usually issued on the same paper and in the same format as the main edition. However, an application differs more from a newspaper or magazine when it uses better quality paper and a convenient format, and therefore has a greater advertising effect.
The subject matter of the appendices is usually related to the information content of the main publication. If it is a popular newspaper, then the supplements are usually devoted to consumer goods and services, for example: "Automobiles", "Recreation", "Household appliances", etc. If this is a specialized magazine, then the appendices can be devoted to the following topics: “Computers”, “Communications”, “Office furniture”, etc.
The printing equipment and distribution system of many foreign publications, even relatively small ones, allows them to produce a sufficient number of regional inserts to meet the needs of advertisers. In Russia, at present, most publications cannot offer their advertisers regional distribution of applications. Many national publications that print their circulation in printing houses in different cities of the country are trying to use this technical feature for the release of regional applications.
Now applications are specially created "for the advertiser", whose product or service does not correspond to the main profile of the publication. So, for example, the Kommersant newspaper has supplements devoted to tourism, food, interior design, and so on. Many of them are distributed free of charge with the main edition, which increases reader demand. Advertising in applications is usually cheaper than in the publication itself, and hitting the right target audience is more accurate. Many publications (especially business ones) produce a huge number of thematic and regional supplements.
Electronic applications, or electronic versions of traditional newspapers and magazines, were born thanks to the birth of the global computer network Internet. Due to the fact that the number of people turning to electronic versions is growing all the time, advertising in them becomes more and more attractive for the advertiser.
For some "advanced" readers, it is not without interest that the publication has an electronic version, on which information from the last issue is duplicated. Sometimes the electronic version is more convenient than the paper version. However, some critics believe that real-time newspapers and magazines will never be able to overcome the "bathroom factor" - you can't get comfortable with your computer in bed, reading from the screen is inconvenient.
On the Internet there are both electronic press and electronic supplements to already existing printed publications. An electronic application is more convenient for readers in terms of searching for specific information. It can be easily found in the archives using a search engine. In addition, the editors of electronic applications get the opportunity to communicate directly with readers through the "chat room".
Generalized advantages and disadvantages of newspaper and magazine publications are given in the table.
Main advantages and disadvantages
press publications

It is important to analyze the procedures for preparing and placing advertisements in the press. In this regard, we can talk about the main stages of these procedures.
- Selecting the form and type of advertising message.
- Choice of specific media.
- Determining the size, format, volume and other features of the advertising message.
- Analysis of texts and layouts of advertising messages of competitors.
- Drafting text and layout of advertising message.
- Delivery of the text and layout to the editor of the selected media.
Designing the layout of an advertising message in the press is a complex creative process. A layout is a schematic drawing, which should clearly show the placement of all advertising elements: headline, slogan, text, image, logo, code, frames, coupons, etc. The layout organizes chaos and, by analogy with an architectural project, is the basis of a future creative advertising work. It is a visual concept that can be revisited and edited many times to achieve the greatest effect. The most common layout style is the dominant image, which takes up 60-70% of the ad area, under which the heading and text block are placed. The logo or code is placed at the bottom of the appeal.
It is possible to combine the dominant image with a group of smaller pictures. Less common are layouts that focus more on type than on art.
Layout development begins with draft sketches - preliminary sketches of layout ideas. From a draft sketch, they move on to an incomplete layout - a full-size layout, on which images and a bold font are presented, while the text is given schematically. The full layout looks like the final version of the advertisement, and finally, the original layout is the final montage, in which each element is exactly in its place, suitable for manufacturing. printed forms. Most often, all these procedures are done using a computer on a monitor screen and printed on a printer.
The most important principle of creating an effective advertising message in the press is the mandatory inclusion in its structure of design elements that attract the attention and arouse the interest of the reader, reasonable, reasonable arguments in favor of the subject of advertising, convincing of its usefulness or prestige, arguments that can create a psychological disposition to purchase and thereby create conditions for turning the reader into a buyer.
Studies show that the most popular among consumers are compositions of press advertisements with the following ratio of elements:
- 60-70% - illustration area;
- 10-15% - header area. The title may be placed above or below the illustration;
- 20% - the area occupied by the text;
- 5-10% - logo area. It is recommended to place it in the lower right corner or at the bottom of the advertisement.
Attracting the attention of readers is largely facilitated by the use different kind drawings, photographs and color illustrations. When illustrating advertisements, the following are used: line drawings; photos; tinted line art; drawings in linocut technique; tone drawings; color illustrations; symbols and styling of titles.
line drawings- the artist works only in black on a white surface. Then this illustration is photo-transformed into an reverse image, i.e. consisting of white strokes on a black surface.
Photos- serve as evidence of an event or situation, as if they are evidence of reality.
Shaded line art and wash line art- darkened areas of a line image are transmitted by toning, which is a raster tone of dots and lines.
Drawings in linocut technique- are often made on the basis of the original photograph. They are very clear, look interesting, reproduce well on rough surfaces.
tone drawings used for ambiance or decorative effect. They are usually done in wash, pencil or pastel.
Color illustrations- may consist of simple color combinations of full color printing.
Symbols and styling of titles also include company symbols and stylized names, sometimes referred to as logos.
More and more research shows that photographs advertise a product much better than drawings. Advertisements are on average twice as likely to be remembered when presented with color photographs. People perceive photos as images real items and situations. Illustrations are preferred to reflect details. Diagrams, tables or graphs should only be used to prove statements and have a specific target group that speaks the language of diagrams.
Intensity- publication parameter and a psychological technique based on the selection of large, noticeable headlines. The reader usually begins the perception of the text with the headline, and a large headline catches the eye faster.
Uniqueness- the principle of distinguishing the figurative, artistic form of a publication or elements of its text from similar ones. The most important facets of uniqueness are originality and novelty. They can be implemented, for example, by placing inverted text, inverted text, etc. The element of uniqueness has more to do with the form than with the content of the advertising message. Its implementation is most often based on the selection of an amazing, unusual, fantastic or bewitching "picture" (such as flying elephants, dogs, etc.).
Dynamics- the use of all kinds of "non-static" images that create the illusion of movement, with elements of an unusual angle, "blurring". Any living organism, starting with a ciliate shoe, reacts sharply to any kind of movement or movement. Such a reaction is inherent in man. Therefore, the images of a woman with hair fluttering from the wind, splashes of champagne, a running athlete, a driving car (hence the “blurring” of the image, understandable to every amateur photographer) attract his attention more.
Repeatability- increasing the power of advertising impact by repeatedly placing advertising messages of the same type with a given frequency (simple repetition) or different in details, but identical in branded constants of messages of the "serial" type (complex repetition).
Contrast- a method of focusing attention on the actual "I" of the company or its product, their distinguishability, distinctiveness, i.e. contrast. "Contrasting" advertising may contain an exclusive (unique) commercial offer, implements ideas such as "Only with us...", "Only with us...", etc. Contrast, in contrast to uniqueness, has more to do with the subject of advertising, content, and not with the design of the advertising message. There is also a narrowed interpretation of contrast by some authors, who reduce it only to the visibility of advertising against a certain background. It is difficult to agree with this. True, sometimes an element of contrast can be successfully “reinforced” by an appropriate artistic illustration (for example, an image of a black woman in a white dress, etc.), although this is not the main tactic for providing contrast.
Size- an external attribute and a visual way to attract the attention of readers. Large messages are perceived faster, and also speak of significant financial opportunities for the advertiser.
Of great importance is the correctly selected color scheme of the design of the "advertising picture". The use of certain colors has various medical, physiological and emotional aspects, as well as cultural and national characteristics. Sometimes, to attract the attention of readers, they use the method of placing a so-called color spot in an advertisement - a uniformly colored spot of a certain shape, which acts as a kind of visual "bait". A good effect can be given by the so-called advertising tape - an ad in a newspaper, located in the form of a low basement across the entire width of the page, or "kauk" - an advertising tape placed at the top of a newspaper or magazine page. In some cases, good results are obtained by placing the so-called island - an advertising message "surrounded" on the page of a newspaper or magazine by editorial materials.
Once the reader's attention is captured, it is necessary to achieve retention of his interest. For an advertising message in the press, the issue of preparing an effective advertising text is very important. The content of the text should grab the reader's attention. This can be facilitated by a catchy, exciting headline, a well-articulated list of "killer" sales arguments, showing how a certain product fits into any lifestyle.
You can make the text initiate good mood, pleasant memories, typing as actor a symbolic or well-known character personifying the product. The text can also provide information about the professional experience and commercial success of the company, the usefulness and high quality of the advertised product, etc.
Summarizing what has been said, we can offer the following six commandments for creating effective press advertising texts2:
- Write texts in which at first sight it will be possible to recognize the advertisement of YOUR company. Remember your position:
- Put all your talent into writing the headline, as well as writing the final part of the advertising text.
- Sell customer benefits, not product features.
- Don't talk about quality and service - demonstrate them to the client.
- Use bright images and expressive language tools! - and the product will "come to life" in the mind of a specific person from your target market.
- Before using a negative approach (criticism of other companies, etc.), humor, obscene language or sex in advertising, consider whether there is another, more effective solution.
A significant impact on the effectiveness of the perception of advertising in the press is the location of advertising on the spread of a newspaper or magazine. Professional advertisers must take into account the so-called Gutenberg diagonal - the trajectory of the reader's gaze, passing from the upper left corner to the lower right corner. According to SR. Haas, for European types of writing, the sequence of perception of information on the spread has its own patterns (see Table 2.4; the numbers indicate the rank of the degree of effectiveness of the place for publication, the first is the highest):
Table 2.4
Hierarchy of advertising effectiveness
on the spread of a newspaper or magazine

As you can see, the most effective is the placement of advertising information on the right side of the spread - 50% (on the left - 33%) of the area. All these considerations can, of course, be taken into account if the issue of the advertiser's financial capabilities, the cost of one module at one or another turn point, etc. is defined.
- Colorful advertisements, regardless of their location (cover, insert, etc.), are always more noticeable than black and white ones.
- Photos advertise a product better than drawings, but their execution should be purely promotional in nature. It has been established that photographs that have won prizes from photo clubs and photo contests, as a rule, do not work in advertising. The photograph of a "star" in an advertisement is only effective for those who can identify with it. For women, a photograph of a child is more preferable than a photograph of a family. The men in the ads don't like the type of girls that the girls themselves like. Enlarged faces may scare the reader.
- The use of techniques and plots of abstract or surreal art is problematic, since it does not directly bring the content of the advertising message to the mass consumer.
- 1/4-page ads stretched into a column are best read. Such forms of arrangement of information as a line or a square are less effective, which is explained by the peculiarities of the human brain.
- The more fonts in a heading or subheading, the less people read them.
- For most readers, oblique text arrangement is undesirable, which can complicate the process of reading and violate the traditional nature of the sequence of perception of words. As a result, the desire to read such a message to the end is sharply reduced.
- High-quality artistic illustrations based on modern technologies(computer graphics, letterpress printing, etc.) significantly improve the perception of advertising messages.
- Consider the layout of the advertising message only when it is completely ready.
Legislation in the field legal regulation advertising in printed periodicals introduces restrictions related to the volume of advertising in publications that do not specialize in messages and materials of an advertising nature (it should not exceed 40% of one issue of a periodical printed edition), as well as restrictions on advertising of alcoholic beverages, tobacco and tobacco products (on the front and back pages of newspapers, as well as on the first and last pages and covers of magazines).
Audiovisual advertising
The historical prerequisites for the emergence of audiovisual advertising were the invention of photography, sound recording devices, cinema, and later video equipment and computers. Audiovisual advertising involves obtaining information through visual and auditory perception and the presence of a wide variety of information media: film and photographic films, slides, magnetic audio and video tapes, laser discs, computer diskettes, etc. It is used as a means of collective and individual influence on potential consumers.
In practice, such forms of audiovisual advertising as films, slide films shown with the help of film and overhead projectors are most often used. These forms are called screen advertising. Widely used at various exhibitions are types of screen advertising, which are various modifications of multi-screen complexes that allow you to project an image onto several screens with various sound accompaniment options (musical and informational), which significantly increases the effect of advertising impact. According to experts, multi-screen overhead projections are especially effective in conditions of a significant level of background noise - at exhibitions, in the foyer of cinemas, conference halls, etc. Sometimes different combinations of audiovisual means can be used: film screening, slide show, light music, acoustic, stereoscopic and other effects.
Promotional films can be in the nature of movie clips, advertising and technical and promotional prestige films. In their production, both classic cognitive or game plots, sketches, as well as elements of computer graphics, animation are used. An advertising film is a short (from 10 seconds to several minutes) film oriented, as a rule, to the widest segments of the population and to advertising of consumer goods. They may be shown before screenings in cinemas or on television. Their production is often based on a wide range of dynamic, action-packed genres and situations.
Advertising-technical and advertising-prestigious films have a longer duration (up to 15 minutes or more), are closer in genre to popular science films and are already focused on narrower groups of target impact. Most commercial and technical films contain information about industrial goods, technical innovations, new technologies, machines, equipment, etc. and are intended for professionals. Unlike them, prestige advertising films mostly tell not about products and goods, but about their manufacturers (sellers) in order to create or strengthen a favorable opinion about them. They are focused not only on specialists, but also on consumers. Approximately the same is classified and advertising video information, the scope of which is increasingly expanding.
Promotional slide films They are demonstrated with the help of a special technique that allows sequentially changing transparencies projected onto the screen, and are usually accompanied by a soundtrack or commentator's explanations. They are used to present the widest range of goods, items for sale at auctions. Slide films are convenient because they allow you to easily change the proposed assortment. Developing means of computer advertising are presentations in the system power point, which have a number of additional possibilities for using special effects.
In addition to the listed types of screen advertising, animated (cartoon) films are very popular, which have ample opportunities for revealing an advertising idea, and are favorably perceived by most consumers (especially young ages). Their viewing is often perceived as a vacation, they are well remembered. In addition, it is possible to overlay different versions of audio tracks on one video sequence.
Other means of audiovisual advertising impact on the consumer are autotypes and autostandists, which allow using certain devices, such as a keyboard, to display information of interest to the consumer on the display or TV screen and receive certain comments in the form of sound, text on the screen, receive necessary information by phone, etc.
Increasingly widespread means of individual audiovisual advertising impact - most often audio and video cassettes, disks and floppy disks. There is a practice of providing them "in addition" to the purchased goods, the use of advertising recorded before a feature film on video cassettes, etc.
- It is not allowed to interrupt the demonstration of the film with advertising, except for breaks between series (parts), in film and video services.
- In case of reference telephone service, advertising may be provided only after the information (references) requested by the subscriber has been reported.
- With paid reference telephone, computer and other services, advertising can be provided only with the consent of the subscriber. The cost of such advertising should not be included in the cost of information requested by the subscriber.
radio advertising
According to 2001 data, radio advertising ranked fifth in the ranking of Russian advertising spending (after TV, press, outdoor and direct mail advertising). The total cost of radio advertising was approximately 55 million USD. In addition, in terms of budget growth rates, radio lags far behind television and outdoor advertising. And this is happening against the backdrop of a significant increase in the number of radio stations. In such conditions, without close attention to marketing research, the "radio business" can hardly be developed.
The means of transmission of radio programs are Various types radio stations with amplitude (AM) and frequency (FM) modulation, most often operating in the ranges of long, medium and short waves. The modern radio broadcasting network also includes cable and digital broadcasting. The transmission of radio signals over various distances, which has the ability to encircle the globe, has made radio a powerful broadcasting medium for mass communication, and, consequently, for the transmission of advertising messages. Radio advertising became available on nationwide networks and local markets. Satellite communications have been added to local and national radio networks, providing excellent quality of radio information transmission.
Advertising messages can be placed both on the radio network and on individual radio stations that have some “free” time. Advertising of radio stations is called "point" and makes up approximately 80% of all radio advertising.
Radio is a highly segmented advertising medium. Even in the conditions of Russia, there are already hundreds of programs aimed at the most diverse tastes of consumers. Radio can be listened to almost anywhere.
Professional American market researcher Michael Hedges segments radio listeners into fans of radio stations, radio, music and news. The most powerful segment is the fans of radio stations (46%), which mainly unites women aged 25 to 44. Radio fans (34%) listen to several different radio stations with no specific preferences. Music fans (11%) are mostly men aged 25-45 and many older people. And finally, the smallest part of radio listeners prefers to listen to news programs and news on several stations for short periods of time. They mainly include people over 35 years of age.
The undoubted advantage of radio advertising is probably the greatest coverage of the mass audience with the help of specialized programs, its use in various parts of the country at almost any time of the day. Radio advertising gives good results for small and medium-sized businesses and younger populations. The coverage of people traveling in cars to and from work is especially effective. The perception of radio advertising practically does not distract the listener from other activities. So, housewives can listen to radio broadcasts while performing a variety of household chores. These broadcasts are perceived much easier than printed messages, due to the lightness, some touch of intimacy and greater naturalness of information transfer. Of all forms of advertising, radio has the most speed and flexibility, the shortest preparation time for advertising. It provides a wide coverage of the population at a relatively small unit price (in terms of costs per 1000 radio listeners). Compared to print advertising, it gives a certain scope to the imagination through sound information, effects and music. Radio ads are less annoying to listeners than television ads.
The disadvantages include fleeting perception, lack of visual images, advertising overload of programs, certain difficulties in planning and buying advertising time simultaneously on different broadcasting channels. If the advertising market is large, airtime can be very expensive.
radio announcement broadcast by the voice of an announcer or actor, can be prepared very quickly and transmitted to radio listeners. It is possible to combine verbal information with musical accompaniment, a sound slogan, certain special effects.
radio commercial- a game plot that reproduces a scene, often using the actors' dialogue. The humorous content turns it into a radio sketch.
Broadcast- a specialized and, as a rule, periodic transmission of an advertising nature within a certain topic, conducted with the participation of manufacturers of goods and services (advertisers), specialists, experts, resellers, consumers.
Due to the significant similarity, the main stages of the organization of radio advertising and recommendations for its organization will be quite clear when highlighting the features of television advertising.
TV advertising
Today it can be argued that now and in the foreseeable future, television acts and will act as a media that has a huge advantage over all other forms of advertising due to the most massive coverage of consumers and the most effective impact on them, combining both auditory and visual perception of information. Television advertising in Russia is developing rapidly.
The TV advertising market accounts for about 50% of the entire advertising market in Russia. The TV advertising market is growing by more than 40% annually. Despite the mass nature of the TV audience, it is still segmented depending on channels, time of day, TV programs and geographical factors. The product is demonstrated in all its colors, functionality, dynamism. The use of television advertising, especially of high professional quality, greatly increases the prestige of advertisers for a number of reasons. Television can create an atmosphere of relevance, success and celebration around the advertised goods and services.
The majority of the population of a number of countries cannot imagine life without television, which has become firmly rooted in everyday life and has become an indispensable attribute of the social environment. However, according to Oxford University psychologist Peter Collet, most people are not "TV junkies." The production of TV ads can have high responsiveness. The process of perception of radio and television advertising does not interfere with other activities (eating, knitting, etc.). Collective listening and viewing of broadcasts can increase the effectiveness of advertising through empathy, the possibility of sharing opinions, etc. On the other hand, it has been found that the more people in the room, the less attention is paid to advertising.
It should be said about the most significant shortcomings of television advertising. The main one is the highest cost of producing television advertising and purchasing airtime. This is largely due to the fact that a large number of people are involved in the creation of television advertising - announcers, cameramen, directors, actors and others, complex expensive equipment is used. None of the existing forms of advertising requires so much experience, skill, knowledge and creativity. In many ways, this is why the cost of an advertising TV commercial can reach hundreds of thousands of dollars, and the broadcast of television advertising can reach tens of thousands of dollars per minute of display. Another major drawback is its highest obsession. It is television advertising that generates the majority of negative assessments of advertising in general.
Data from a selective all-Russian survey of 3,000 Russians conducted in 2002 showed that 66% of viewers perceive television advertising negatively, 9% have a positive attitude towards it, and 23% are neutral (indifferent). A serious drawback is the limited choice of advertising information of interest to the viewer - “look what they show” (lack of selectivity). You can sit at the TV screen for years and not see the information you are interested in. The previously mentioned “transience” of information is also characteristic, which often interferes with the perception of the meaning of an advertising message, and sometimes forces you to keep stationery on hand to write down an address, phone number, bank account, etc. The negative side of the mass nature of television advertising is manifested in the fact that advertising targeted at the wealthy segments of the population causes a negative reaction among the population with low incomes.
Various technologies for monitoring television advertising have already been introduced into Russian practice. They are implemented primarily by TNSGallupAdFacfa RPRG companies. The first monitors TV advertising in 18 cities of Russia, the second - only in Moscow. The methods are similar: all TV programs are recorded around the clock, and then viewed and analyzed. The TNS Gallup AdFact methodology provides for the so-called double processing of the air: the cassettes are viewed by two independent operators and the results are compared in order to determine the correct measurements (indicators). This reduces the role of the "human factor" in the analysis.
TV screensaver- a short still image of an advertising message, trademark or logo on the screen, for example, against the background of a clock in front of an information program.
TV commercial- the most common and expensive type of TV advertising, a mini-movie, a game plot, lasting from 10 seconds to several minutes, a kind of work of directing and cameraman's art with the involvement of actors, the use of musical accompaniment, special effects, etc.
TV report- a television advertising report from the scene of some events (exhibitions, presentations, fashion shows, from a store, etc.), as a rule, accompanied not only by showing the subject of advertising, but also by expressing the opinions of the reporter, visitors, consumers, sellers, etc.
TV show- a specialized television broadcast of an advertising nature within a certain topic, conducted with the participation of manufacturers and sellers of goods and services, specialists, experts, resellers, demonstrators, consumers. It is often broadcast on television in recordings and with repetitions (“TV Shop”, “Shop on the Couch”).
- Select the type of advertisement.
- Channel selection.
- The choice of the program before, during or after which the advertisement will be broadcast.
- Broadcast time selection.
- Selecting the moment of transmission of the message.
- Solving the issue of the duration and frequency of the advertising message.
- Analysis of advertising messages of competitors.
- Preparation of the selected type of message.
- Broadcasting on the air in accordance with clause 5.
- The object of the appeal must be a specific viewer. Direct appeals to the audience are both simple and effective.
- Advertising should be simple, and one commercial ad should not cover more than 1-2 topics. The tone of your ad should reflect the personality of the product.
- An advertising message should start with the most interesting. The first 5-10 seconds of the transmission should immediately draw attention to your ad, then it becomes more difficult to do so.
- During the broadcast of advertising, you need to repeat the name several times or show the advertised product. It is necessary to observe a dynamic approach and the logic of presenting information (preferably according to the “what, how (when), where”) scheme. Long-term advertising campaigns require permanent heroes (the Haggis cowboys, Aunt Asya).
- Musical accompaniment and colors should not distract from the perception of information, but serve only as a background for the advertising message. Music ads should be avoided if the music is of poor quality.
- It is desirable to demonstrate how the advertised product solves specific problems (Ariel, Tide, Comet). Eyewitness accounts are of great importance (Rama, "Golden Skate").
- In TV advertising, frames are more important than text. It is advisable to choose one frame that visually summarizes the entire video, and put it at the forefront.
- Audio and video information should differ somewhat in its structure.
- The announcer is better off behind the scenes.
- Reading information must be framed so that it can be read at least 3 times, and the display of the phone number must be at least 8 seconds long.
- The audience is more interested in looking at faces, not buildings. Close-ups are the most interesting and effective. Do not get carried away with an abundance of plans - it is expensive and difficult to perceive. Mass scenes, as a rule, attract less attention than showing one person.
Compliance with these recommendations in high-priced television advertising is especially important. The cost of an advertising clip in the United States is hundreds of thousands of dollars and, according to D. Ogilvie, it takes 2 to 5 days on average to produce an 11-13-hour working day. The use of computer graphics can significantly reduce costs and time, however, the abuse of its techniques leads to a weakening of the impact on the emotions and feelings of the audience, so advertisers often switch to old technologies, appealing to the heart and mind of a person, using the power of a live visual impact.
- In radio and television programs it is not allowed to interrupt with advertising:
- children's and religious programs;
- educational broadcasts more than once within 15 minutes for a period not exceeding 45 seconds;
- radio shows and feature films without the consent of the copyright holders;
- broadcast in live broadcasts, the list of which is established by the Federal Law of the Russian Federation "On the procedure for covering the activities of state authorities in the state media";
- other programs, the duration of which is less than 15 minutes;
- other programs, the duration of which is from 15 to 60 minutes, more than twice.
- When using advertising in the form of overlays, including the "creeping line" method, its size should not exceed 7% of the frame area.
- Distribution of advertising of the same product, as well as distribution of advertising about the advertiser himself, should not be carried out more than twice total duration no more than two minutes during an hour of air time of a radio and television program on the same broadcast frequency.
- In radio and television programs that are not registered as specializing in messages and materials of an advertising nature, advertising should not exceed 25% of the broadcast volume during the day.
Outdoor advertising
Outdoor advertising, the oldest form of advertising, remains one of the most common forms of advertising for goods and services to this day. In Europe, the cost of it is up to 15% of the advertising budget and second only to the cost of advertising in the press and on television.
Outdoor (external) advertising includes various types of advertising displayed outside the interior (dwellings, offices, etc.). It appears most often in the form of posters on billboards, signboards, posters, billboards (elements of outdoor billboard advertising, which are a special design that can be mounted on fences, walls of buildings), which should be placed in crowded places, along streets, highways, at the ends of buildings, in the form of various kinds of shop windows, etc.
Outdoor advertising is highly visible and due to its size and design, use of light, bright colors, animation, has a significant impact on consumers. The scale of the image of objects significantly exceeds their real size, which in itself is a potent factor. The intensive movement of people past large-format posters (on foot or in transport) enhances the impact of outdoor advertising. Its exposure time under certain conditions is 24 hours a day. Outdoor advertising can target different types of consumers, such as housewives on their way to the shops, businessmen on their way to and from work, tourists on their way to the airport, and so on.
The disadvantages of mass outdoor advertising include, first of all, the fact that the time of its real perception, especially for those traveling in transport, is very small (a few seconds). Outdoor advertising media are subject to deterioration due to weathering and vandalism. On average, the cost of outdoor advertising is very low, but with its mass production and placement, it can amount to significant amounts.
The allocation of space for outdoor advertising, as a rule, is carried out in agreement with the municipal authorities, who approve its certain forms and layouts in accordance with applicable law. Distribution of outdoor advertising is allowed only if there is a decision of a competent government agency or a local government agreed with the relevant territorial division of the traffic police of the Ministry of Internal Affairs Russian Federation or governing body railways(when advertising is placed in the right of way of railways). It, as a rule, provides for the issuance of a special passport or permission for the placement of advertising, as well as coordination with a number of architectural and urban planning organizations. A set fee is charged for issuing a permit. Placement of outdoor advertising on any object (building, structure) is allowed only on the basis of an agreement with the owner or holder of another real right to this property.
In order to ensure safety traffic Temporary requirements for the placement of advertising on roads and streets were approved, which define general and additional requirements for the distribution of advertising on the road network, approximate symbols and inscriptions on advertising and service signs, the procedure for coordinating advertising distribution sites, the form of the coordinated outdoor advertising magazine and the rules for filling it out. In accordance with this act, it is prohibited to distribute advertising that makes it difficult to assess the real traffic situation and is similar to the technical means of organizing traffic and special signals. Advertising must not restrict the visibility of these technical means or interfere with their perception; cause blinding of road users, including by reflection; to reduce the dimensions of spans of engineering structures; be located in such a way that for its perception pedestrians were forced to enter the carriageway of streets and roads.
An effective organization of outdoor advertising placement focuses on taking into account such parameters as the viewpoint (their number should be maximum), the angle of view and OTS. The angle of vision is different for a person traveling in a vehicle and a pedestrian, for a driver and a passenger, for a pedestrian walking in a crowd and a lone pedestrian, for a person traveling in a car, truck, bus, etc. The angle of view is especially important to consider when choosing the height at which advertising signs and billboards will be located. OTS indicator (opportunity to see) - the number of contacts with an advertising medium, expressed in thousands. It is sometimes referred to as Gross Impressions. At its core, OTS is the number of "realized" viewpoints, including recount, since OTS is calculated for a certain period (hour, day).
Outdoor advertising is most often used by trading houses and shops, cafes and restaurants, wholesalers, exhibition organizers, etc. It is preferable that outdoor advertising be designed brightly and catchy, illuminated in the evening and at night, be extremely simple, quickly and easily digestible, and not provoke traffic accidents. To ensure speed and ease of perception, the entire advertising composition should contain no more than 3-4 design elements (company name, slogan, line of business or type of advertised product, address part). Inscriptions, their format should ensure correct and quick reading. This is usually an easy-to-remember phrase with a small number of words (some people think that there should be a maximum of 7 words). Outdoor advertising designed for pedestrians can be more extensive, and in places of long-term congestion of people (train stations, bus stops, department stores) contain even more information.
Outdoor advertising should, on the one hand, successfully "fit" into the environment, harmoniously combine with the objects surrounding it, and on the other hand, stand out and catch the eye, which is quite difficult to achieve at the same time. The volume of advertising information and the form of its submission in outdoor advertising have limitations associated with the speed of movement of the advertiser. For a pedestrian, the time of perception is approximately 5-10 seconds, for a person traveling in transport 1-3 seconds.
Almost the entire set of outdoor advertising media is typical for most large Russian cities:
- shields of all sizes and shapes;
- various installations of illuminated advertising;
- so-called roof installations;
- electronic scoreboards and newspapers;
- ticker;
- video walls;
- cabinets;
- decorative street clock;
- all kinds of light boxes on poles;
- signs, signs;
- installation and stretching over the carriageway of the street;
- kinematic installations;
- volume-spatial installations;
- steles;
- outdoor advertising at public transport stops;
- outdoor advertising on sports facilities;
- outdoor advertising on transport.
The most common billboard advertising in the form of posters and billboards (painted stands). Its main type is a large-sized standard poster (30 sheets, approximately 6.6 x 3 m in size). Posters are printed using lithography or silk screen printing and then pasted onto billboards. 30-sheet posters are now increasingly losing ground to 8-sheet posters. The practice of sequential (every 50-100 meters) placement of posters of the same type is becoming more widespread in order to gradually perceive their individual elements. Advertising boards are drawn by artists by hand at their location or in workshops. The advertising board has a larger area and is more extended in length than the poster (the proportion of the poster is 2.25:1, and that of the advertising board is 3.5:1). Standard size advertising board is approximately 14 by 4 m.
- Billboard advertising is dedicated to only one product.
- Billboard advertising should catch the eye in the first second, be remembered quickly and for a long time. It should shock the viewer with its size, execution, clarity of the text.
- Billboard advertising does not recognize subtleties. Therefore, the use of words with double meanings and complex drawings is unacceptable. The content of billboard advertising should be understandable to the majority of consumers.
- The advertising text should be short, concise and include no more than seven words.
- The pictorial part, as a rule, should include only one picture without excessive detailing. The picture should speak about everything and be perceived absolutely unambiguously even without advertising text.
- The general style of billboard advertising should be consistent with the style of other types of advertising for this product. This provides the effect of accumulation of individual advertising influences among consumers.
Volumetric, moving or rotating structures and inflatable objects have long been popular in outdoor advertising. Currently, the practice of a special type of night illumination is being developed, in which the background of the shield seems to disappear and the image is perceived against the background of a black sky. Some advertisers are experimenting with holography, in which an image projected from one billboard to another creates a three-dimensional perception of objects. Chilean advertisers have come up with an original way, thanks to which posters placed in subway tunnels are perceived by passengers moving in cars as 7-second animated films.
Sometimes the so-called rotation is used, i.e. moving the shield from place to place. It is especially effective in relatively small settlements with low rates of commuting, where the same contingents of people follow the same routes for a long period of time (to and from work, to shops, etc.). Tobacco and wine companies, whose advertising on television is prohibited, and retailers often resort to billboard advertising. The relatively low cost of billboard advertising attracts small and medium-sized firms.
A special place is occupied by advertising on the walls of buildings and structures, most often in the form of firewalls. The seller for the placement of wall advertising is the company - the owner advertising space on a specific wall of a specific building. At the same time, the chain of "customer-carrier" relationships also includes the balance holder of the building and the city. The first is due to the fact that he is the owner of the wall, and the second - because it is about the exploitation of urban space. A simplified scheme for the sale and purchase of these media looks like this: the contractor buys the space on the wall from the balance holder, pays the city rent for this place in accordance with the current city tariffs, and then sells it to the client for a certain period of time, for example, a year. There are situations when, after the agreed period, the contractor does not remove the firewall, continues to service it and pays the city for rent and even for electricity. This is due to the fact that "developed" places are more in demand compared to a bare wall, which is much more difficult to sell.
The most traditional term for wall RK is one year, although there are smaller ones (up to three months) and longer ones (up to three years).
Illuminated advertising is a kind of billboard advertising used in the evening and at night in the form of electrified or gas-lighted light displays. Possessing high contrast and significant dimensions, illuminated advertising is the most attractive, memorable and spectacular type of outdoor advertising.
The leader in illuminated advertising is most often considered the United States, whose cities sparkle and shimmer at night with all conceivable and inconceivable colors of thousands of illuminated advertisements. In general, the original samples of illuminated advertising create a unique night aura for American cities.
Illuminated advertising is visual and spectacular advertising, and it is even less disposed to long texts than billboard advertising. Most often, illuminated advertising is limited to the name (brand) of the product or a super-short phrase, which is placed against a background that ensures its effective and effective perception.
Rooftop installations are advertising structures big size, which are mounted on the roofs of urban buildings. For example, in Moscow (on Leningradskoe shosse) the largest roof-top installation in Europe was installed with an advertisement for Samsung Corporation. In the evening, this luminous giant canvas is clearly visible at a distance of 5-6 km. Tens of thousands of drivers and passengers of land transport watch this advertisement every day.
Advertising on transport
Advertising on transport can be internal and external. The main requirement for the placement of outdoor advertising on transport is perceptibility in traffic conditions. To ensure recognition, similar design techniques are used: logo image, application corporate colors, special lettering, etc. In the production of this type of advertising, it is necessary to take into account the capabilities of a sufficiently large number of people with visual impairments. A variety of external transit advertising is also a basorama - an illuminated advertising panel installed on the roof or around the perimeter of buses, trolleybuses, trams. Internal transit advertising in public transport most often uses the car map format. Usually such cards are oriented horizontally at a height of about 30 cm and a length of about 70, 100 or 140 cm. Due to the long period of perception of this type of advertising, it can use voluminous and complex messages. The main requirement for the quality of such advertising is also related to the size and clarity of the font.
Until the end of 2002, the public transport advertising market was decentralized: advertising firms worked directly with transport companies. The market (estimated at that time at 8-10 million dollars) was practically controlled by 5-6 large companies - New Ton, Transcom, News Outdoor, etc. In October 2002, a new partner appeared in Moscow - the state unitary enterprise (SUE) "Advertising and Information on Transport", which becomes the only intermediary in the market of production, placement and dismantling on the transport of the capital. Moreover, according to the decree of the Moscow government, the cost of monthly placement on one machine will be at least - 2.5 thousand rubles, maximum - 13.2 thousand rubles. (excluding VAT).
According to the rules for the distribution of advertising on vehicles it must be carried out on the basis of agreements with the owners of vehicles or with persons who have rights in rem to them. The main requirements for placing advertisements on vehicles and the procedure for exercising control are determined by the Instruction No. 410 approved by the Order of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation of July 7, 1998 on the placement and distribution of outdoor advertising on vehicles. Placement is limited to the following locations: roof, body sides up to a certain line, fuel tanks and motorcycle toolbox covers. Advertising should be placed on an area not exceeding 50% of the painted surface of body parts. Advertising should not block external lighting devices, side numbers, limit the visibility of the driver. The form of the Journal of accounting for advertising placement on vehicles has been approved.
Advertising on consumer goods
This type of advertising is widely included in our everyday life. An important requirement for its organization is a certain harmony between the consumer properties of the product, on the packaging of which the advertisement is placed, and the nature of the advertising message (advertised product). There is no doubt, for example, the inappropriateness of advertising tobacco products on the packaging of medicines, etc. Widespread and significant effect gives advertising on plastic bags, especially when good quality the material from which they are made, and the printing performance of advertising.
- Manned flying objects (aerostats, airships, balloons, etc.).
- Airborne unmanned objects (usually tethered to the ground).
- Objects fixed on the ground, roof, special stand (static, dynamic and with moving elements).
- Inflatable suits with a person inside.
A new type of outdoor advertising is advertising on the floor, which was first used by some large American supermarkets at the suggestion of advertising specialists who noticed that customers, moving around the store, often look at their feet. Advertising is also used on the asphalt of roads and sidewalks, racing tracks (the latter has been banned since 2003 by the decision of the International Motor Sports Association - FIA in connection with the appeal of the union of pilots, headed by M. Schumacher).
In recent years, an unusual and very expensive type of advertising has appeared abroad - advertising on the body spaceship. Very few people see such advertising, but it is a great prestigious advertisement, since only very powerful and prosperous firms can place it.
Total monitoring of outdoor advertising in Russia is carried out by RPRG (30 cities) and ESPAR-Analytic (50 cities). It is based on computer geographic information systems (GIS), which allow to reproduce maps of cities, on which locations and types of outdoor advertising are marked. Employees of monitoring companies meter by meter bypass and examine all the streets and lanes, photographing and fixing the parameters of each type of new, unrecorded "outdoor".
Monitoring is carried out in the first half of each month. Most of the posters are pasted on billboards by the 1st, and by the 4th-5th all advertising images are replaced with new ones. Observers of "ESPAR-Analyst" collect data from the 4th to the 12th of each month, and in RPRG, approximately 7 to 12 days are allotted for this. There is one nuance here: if the RK starts on the 15th of the month and lasts for two weeks, it, of course, is not tracked. The growth of the HP market may necessitate monitoring twice a month, which will increase the accuracy of measurements.
- Outdoor advertising should not be similar to road signs and pointers, worsen their visibility, as well as reduce traffic safety.
- The distribution of outdoor advertising is allowed with the permission of the relevant local government and must be coordinated with the authorities of roads, railways and the Ministry of Internal Affairs.
- For the issuance of permits for the distribution of outdoor advertising, a fee is charged in the manner and in the amount established by the relevant local government in agreement with the listed bodies. At the same time, the amount of the fee should not exceed the cost of carrying out work on issuing permits for the distribution of outdoor advertising, determining the places for its distribution and monitoring the state of outdoor advertising and technical means of stable territorial placement.
- Distribution of outdoor advertising is carried out on the basis of an agreement with the owner or with a person who has property rights to the property. Distribution of advertising on vehicles is carried out on the basis of agreements with the owners of vehicles or with persons who have property rights to vehicles.
- Cases of restriction and prohibition of distribution of advertising on vehicles in order to ensure traffic safety are determined by the authorized bodies that are entrusted with control over traffic safety.
An interesting commentary to the law "On Advertising", proposed by Yu.Ya. Voldman. In the literature on advertising, the following features of outdoor advertising are noted. Some authors indicate that this is a means of influence that allows you to overtake a person not at home or in the office, but on the street or during trips. In today's mobile society, outdoor advertising meets a large part of the population. At the same time, they recognize that, as a rule, the main function of outdoor advertising objects is to reinforce and supplement advertising placed in other media by reminding the brand of a product or company name. Others believe that outdoor advertising is “money thrown away”, that it is not operational, since one paperwork takes several months.
At the same time, the indispensability of outdoor advertising is noted if you want to introduce your company to residents of a certain area, those who drive along a given highway or walk along a given street, or indicate the place where your office is located. Outdoor advertising media have a clearly defined audience, which can be conditionally divided into two categories. A pedestrian will not pay attention to a street billboard, no matter how big it is, but their eyes will definitely be attracted by a poster at a bus stop or billboard. In the same way, a motorist will not notice advertising installations standing on the sidewalk, because he can see street billboards, panels-brackets on lighting poles, roof installations and firewalls.
In connection with the publication in the Mir Novosti newspaper on October 7, 1996 of an article by F. Perfilov “Mooing Advertising”, the question arose of whether it should be attributed to outdoor advertising of various companies on plastic capes “put on” cows and other animals that graze near the highway, where there are a lot of traffic jams, and in other places suitable for advertising goods and producers. It seems that for the same reasons as shop windows and other types of advertising mentioned above, “mooing advertising” cannot be attributed to outdoor advertising. As stated in paragraph 2 of Art. 14, the distribution of outdoor advertising in urban, rural settlements and other territories is allowed with the permission of the relevant local government.
However, the competence of local governments includes not only giving permission to place outdoor advertising. In the decision of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation of March 4, 1997 on the case of checking the constitutionality of Article 3 of the Federal Law of July 18, 1997 "On Advertising", it is noted that on the basis of Articles 130, 132 and 133 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation, local governments have the right to independently resolve local issues related to the peculiarities of the distribution of outdoor advertising, since they affect the authority to use, own and dispose of municipal property.
The advertiser and the advertising distributor have the right to demand from the local government authority issuing permits for the distribution of outdoor advertising, documentary evidence that, in accordance with Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of February 2, 1996 No. 105 "On Approval of the Regulations on the Procedure for Establishing Land Use Boundaries in the Development of Cities and Other Settlements" and the law on land management of the relevant subject of the Russian Federation, the land on which outdoor advertising will be placed is municipal property.
There may be cases of placing outdoor advertising in the sea and on rivers, as well as near sites intended for aircraft. In this case, it seems that permission to place advertising should be issued by the relevant local government after agreement with the relevant authorities of sea, river or air transport. Perhaps the legislator will pay attention to this omission in Article 14 of the Law "On Advertising" when deciding whether to amend and supplement it.
Currently, using their rights, which were discussed above, local governments adopt regulations that determine the features of the distribution of outdoor advertising in their territory, the procedure and amount of fees for issuing permits for the distribution of outdoor advertising. It seems that these provisions, based on the proposals published in the press, should:
- establish zones with restrictions on advertising (for example, the historical centers of cities and other settlements, areas near temples of various faiths, etc.). Establish that theatrical, museum, philharmonic advertising can be distributed in these zones;
- establish a higher fee for permits to advertise alcoholic beverages and tobacco products, taking into account the harm they cause to health;
- establish a higher fee for placing outdoor advertising in places where the speed of vehicles is lower than usual (at traffic lights, crossings, traffic police posts and other similar places).
And one more circumstance that deserves attention. In some cities, local governments take decisions obliging advertisers and advertising producers to conclude contracts for the distribution of advertising not with the owners of the relevant property, but with the city's local government. At the same time, such a non-legal concept as "advertising space" was introduced, which supposedly belongs in all cases to the local government. Such, so to speak, "order" is established, for example, in the city of Yekaterinburg. This order is contrary to paragraph 3 of Art. 14, which provides for the conclusion of contracts for the placement of outdoor advertising only with the owners of the relevant property.
promotional souvenirs
Promotional gifts are an effective means of promoting and advertising the organization that gives them. Almost every firm makes extensive use of this form of advertising. According to some estimates, about $3 billion worth of souvenirs are produced and distributed annually in the United States. The mere fact of presenting an advertising souvenir (already rarely seen as an offering or a bribe, although such points of view are sometimes encountered) greatly emphasizes the advertiser's solidity.
An advertising souvenir should be distinguished from a prize, the recipient of which does some kind of favor to the advertiser - purchases a product, sends a coupon, attends a product demonstration, etc. Unlike a souvenir, as a rule, there is no advertising text on the prize. Advertising souvenirs are distributed free of charge, they act as “models of good will”, remind the consumer about the company, thereby (sometimes for a very long time) performing advertising functions.
Souvenirs, which are carriers of advertising information, facilitate the possibility advertising contacts not only with the "object of donation", but also with the people around him: colleagues, family members, partners. In order for an advertising souvenir to successfully fulfill the functions assigned to it, it must correspond to the needs, tastes, habits, social and professional status of the partner. It is desirable to have company symbols, company name, slogan, address data of the donor company (address, phone, fax) on it.
Since most people associate the quality of a souvenir with the solidity of the company, there is a tendency to increase the average cost of souvenirs.
Taking into account the function of satisfying some needs of a real or potential partner, fountain pens, various kinds of desktop items or stationery sets, writing pads, penknives, lighters or ashtrays (for owners of this bad habit), calculators, key rings, T-shirts, bags, etc. Good results gives the practice of systematically giving souvenirs, calendars, notebooks to permanent partners or clients for Christmas or New Year, for anniversaries. For particularly significant partners, the company can afford to present more expensive souvenirs: business folders, cases, works of art.
The practice of independent production of souvenirs is available to a few organizations. More often they resort to the system of ordering souvenir products with the necessary attributes or to the purchase of these products and their subsequent “finishing” by equipping them with branded stickers, engraving, etc.
The packaging of souvenirs is of no small importance - boxes, wrapping paper, bags, plastic bags, etc. with branding of the donor.
The donating company must ensure proper storage and accounting, a clear procedure for the distribution and issuance of souvenirs, which allows you to trace the nature of the use of material and financial resources and the system for distributing promotional souvenirs, which is one of the factors to increase the effectiveness of the advertising campaign.
Print advertising is an older form of advertising than print advertising. This is historically the first form of mass advertising. Print advertising and advertising in the press are united by the identity of the media (paper or its substitutes) and the nature of its perception (through reading). However, their main difference is that print advertising does not belong to the media and does not have such mass distribution channels as newspapers and magazines, and therefore, as a rule, is focused on narrower consumer groups. To assess the feasibility of using print advertising, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of the reading audience and the group of target impact, knowledge of the main goals advertising company, the subject of advertising, regions of distribution, circulation, labor intensity and financial capabilities of the advertiser and, of course, the areas of preferred use of its individual types.
Leaflets and brochures are handed out at the point of sale or service, distributed through hotels, shops, cafes, restaurants, post offices, banks and other public places. Use print advertising and direct mail (direct mail).
In black and white and without illustrations, print advertising is relatively cheap. Expensive print advertising looks more prestigious, provided with illustrations, especially color ones, although high quality printing and paper, as well as an abundance of color photographs and graphics, do not make advertising more effective, but create a more pleasant image and impression of the company, which naturally affects popularity.
2. Duration of exposure: The reader can refer to the advertising message in a week, a month, a year after the publication of the advertisement. You can save the advertisement, view it later, show it to a friend.
3. Thematic targeting: A large number of publications on the market allows you to choose a highly specialized media specifically for your product and target audience.
4. Geographic targeting: The presence of print media even in the smallest settlements and certain areas of large cities. Possibility of advertising on a specific territory. Further development of this advantage allows you to advertise in many local (district) media, indicating in each of them the address of the nearest office (shop).
1. Weak channel of influence: Impossibility of influence on the auditory channel of perception (no sound), weak influence on the visual channel (no dynamic visual objects).
2. Small audience: Even the most popular publications, such as TV Guides, have an audience several times lower than the audience of an average TV channel. Thematic publications, as a rule, come out in very small circulations.
· Catalog;
· Poster (billboard);
An informational (advertising) letter is written on a letterhead and is addressed to a specific person. Contains information about the company, the main directions of its activities (about the most important goods, services, etc.) and the goals pursued by writing this letter, that is, those actions that can be expected from the recipient. In an advertising letter, you can offer the addressee to sell a product, provide a specific service, inform about price cuts, discounts, new partners, branches located near the addressee, offer cooperation, etc. The letter can be individual and typical (the text is addressed to several recipients, and the name of each is printed at the top of the letter indicating the position, surname, initials, etc.).
An information sheet is similar to an information letter, but does not contain the recipient's attributes. Letterheads for writing it are usually not used. Brand name, logo and corporate colors can be used as design elements. Includes data on prices, discounts, benefits, etc. Since the information sheet is addressed not to a specific person, but to persons who are only supposedly interested in the proposal, the presentation of the essence is simplified, but the main characteristics and comparison with analogues are presented quite fully.
The flyer contains advertising information, is brightly designed, has a capacious advertising text. Often, when decorating it, they resort to funny, funny drawings, place an advertising slogan on it. Its main function is to be noticeable, to catch the eye. A flyer is similar in principle to an advertisement in the press, but at a lower cost it can be much larger and describe the subject of the advertisement in more detail.
A booklet is a well-designed promotional material about a company or a specific product (service) or group of them. Small in volume, often A4 format with a 6-page fold. To a greater extent, it refers to advertising materials of a prestigious orientation, often issued by firms that have achieved certain successes, or on anniversaries.
Usually in booklets, information is presented in the form of visual images (photos, drawings and diagrams) and text that explains and supplements them.
To date, a booklet is almost the most popular type of promotional printing products, since at a relatively low cost it outperforms a leaflet in terms of efficiency. The booklet is compact, it is convenient to take it with you from the store or from the advertising stand. It fits easily in an envelope, so it is optimal for mailing list. Booklets are usually printed on fairly thick and high-quality paper. It is colorful and informative.
Due to its obvious merits, an advertising booklet ends up in the addressee's office or home more often than, for example, a leaflet, which can be easily crumpled up and thrown into the nearest garbage container. Therefore, if your goal is not just to inform the public about any event, but to deliver high-quality information about a product or service to a potential consumer's home, it is better to order booklet printing.
Flyer. As well as the booklet, to a greater extent refers to promotional materials of a prestigious, image character. More voluminous than a booklet (most often up to 10 or more pages), contains many color photographs and drawings. Often issued for a new type of product or for anniversaries. Sometimes it contains information of an economic, financial nature, photographs of company executives.
Prospectuses can be commodity, tourist, trade, etc. A special type of brochure is a folder - the simplest and cheapest type of brochure, intended for mass distribution. It usually consists of one sheet, sometimes folded in half, with short text, simple illustrations and graphics. In the form of a prospectus, annual reports, balance sheets of a company (bank) are sometimes drawn up. It is believed that booklets and brochures are either made of very high quality or not released at all.
The promotional brochure is an extended brochure of 20 or more pages with more detailed information about the characteristics of the product. An advertising brochure is sent out or handed out to encourage participants in advertising contests, at exhibitions, applied to purchases, newspapers, magazines.
An advertising brochure allows you to achieve a much more serious advertising effect compared to a regular advertising booklet. Binding, a larger amount of text and graphics in an advertising brochure will reveal the advertised item or service more deeply and more attractively than a regular leaflet or booklet.
Catalog - printed advertising material in the form of a booklet or magazine with a list of goods and services, illustrated with their descriptions and photographs. Most often colorfully designed and easy to use. The catalog does not always indicate the prices of goods due to the fact that it can be calculated for a long period of use, during which they may change. A variation of the usual catalog is the so-called address catalog - an informational printed publication that contains complete lists of organizations, enterprises, firms of any industry (a number of industries) in a particular region or throughout the country. It is used in the organization of direct mail advertising.
The catalog may be intended for consumers, trade and other organizations. It may be widely used in the mail order business or be purely informational or technical in nature.
There are well-known "smelling" catalogs of perfumes, "playing" catalogs (of musical works, notes, etc.).
A poster (billboard) is a catchy, as a rule, large-format image, accompanied by a short text, made for propaganda, advertising, informational or educational purposes. In modern design, the poster is perceived as "a message summarized in a clear visual formula, intended for conclusions and concrete actions."
The features of the genre include the following: the poster should be visible at a distance, be understandable and well perceived by the viewer. The poster often uses an artistic metaphor, figures of different scales, images of events taking place at different times and in different places, contour designation of objects. For text, the font, location, color are important. The posters also use photography in combination with drawings and paintings.
The main elements of print advertising are the textual and artistic basis. The font is chosen based on many considerations: ease of visual perception, attractiveness, mystery, the general creative idea of the message, etc. The artistic design of printed advertising, the use of photographs of drawings, color combinations, etc. is also of paramount importance.
The work contains a synthesis of psychological, psychophysiological and marketing approaches to motive and motivation, original approaches to determining consumer motivation, a comprehensive author's analysis of the consumer as an individual with unique personality characteristics and complex psychological features, consumer segmentation and classification according to various criteria, impact characteristics external environment on the consumer, a detailed consideration of the mechanism for the consumer to make a decision to purchase goods. It is intended for students of economic, managerial, psychological specialties of universities, graduate students, teachers, managers of the industrial and economic spheres, marketers, and everyone interested in the problems of consumer motivation. The materials of this book are recommended for specialties: 061500 - `Marketing`, 061100 - `Management of the organization`, 060800 - `Economics and management at the enterprise (by industry)`, 060100 - `Economic theory`, 351300 - `Commerce ...
Over the past 20 years, customer satisfaction and loyalty has become one of the fastest growing areas of market research and interest continues to grow. Organizations today are investing heavily in programs aimed at retaining customers, as the preservation and increase of company profits depend on it. The book "Measuring Customer Satisfaction: How to Know What People Really Think" is a guide to this vast area. It discusses methods for studying customer satisfaction, both from the perspective of the client and from the perspective of a research service provider. Among the many topics and issues explored by the author, the following can be distinguished: modern theories underlying the study of the degree of satisfaction and constancy of consumers; how to formulate research requirements; what questions the agency needs to solve before offering its services in conducting...
World-famous branding guru David Aaker advises on how to beat the competition and become a leading brand in your market. In this groundbreaking book, Aaker describes the concept of brand relevance: characteristics that determine its strength, opportunities for promotion, barriers to competitors. Using the example of leading companies such as IKEA, Zara, H&M, Toyota, Yamaha and others, the author shows how to make your brand dominant in the segment, leaving competitors out of business. The key points of the publication: when managing a product in a new segment, treat it as if it were already a brand; if you can't produce what consumers want, or you lose momentum and visibility, your brand becomes unclaimed; use innovation to create barriers to competitors. Instead of being the best, be the only brand in your niche, making competitors irrelevant.
Knowledge of the characteristics of consumer behavior is the starting point of all marketing activities. When developing a product strategy, company leaders need to know the reaction of consumers to their products. This tutorial sets out the basics of this science, while focusing on such an industry as services. Each chapter ends with questions and tasks designed to test the material studied. At the end of the book are tasks, tasks and tests for practical exercises. For undergraduate and graduate students of relevant specialties, as well as for entrepreneurs, whose success in the market is unthinkable without knowing the reaction of buyers to the goods and services offered.
A critical analysis of the existing requirements of energy supply organizations to consumers is given. electrical energy connected to the power grid. The existing practice of drawing up energy supply contracts, as well as the experience of implementing non-contractual relations between electricity consumers and energy supply organizations, is considered. Discussed are the possibilities of reducing the costs of consumers for connection to power grids and in the process of drawing up contracts for energy supply. Unacceptable, but, unfortunately, applied in practice methods of unauthorized connection to electrical networks and electricity consumption are described. For specialists of organizations - consumers of electrical energy (including individual entrepreneurs And individuals), energy supplying (energy sales and power grid) organizations, bodies of Rostekhnadzor, as well as design, installation and commissioning organizations.
Starting your own business is not an easy task: everything works out only for the most persistent and talented. About what makes up success in business, and tells this book. These are 99 bright stories of foreign and domestic entrepreneurs who managed to offer consumers a solution to their problems and proved to the market the need for their product. The authors of this book, Kommersant FM radio hosts Mikhail Khomich and Yuri Mitin, not only brought together stories about successful businesses, but also identified a key success factor in each case: a new business idea; successful business model; proven strategy; accurate marketing ploy. The book will serve as an excellent practical guide for anyone who is thinking about creating own business, and those who have already opened their own business will be able to take note of the solutions described in it. The publication will be of interest to anyone who wants to learn more about successful entrepreneurs, companies and business ideas of our time. It...
noah activity.
Purposes of advertising activity.
History of advertising.
Types of advertising.
Legal base of advertising activity.
General requirements for advertising.
Features of advertising of certain types of goods.
Theories of communications and their application in advertising.
Advertising campaign: planning and implementation.
Evaluation of the effectiveness of advertising.
The main subjects of advertising activity.
advertising market.
The role and functions of the advertising service
The role and functions of advertising agencies.
Classification of agencies by type of activity
Organizational structure of an advertising agency
Features of the advertising campaign.
Stages of an advertising campaign.
Factors determining advertising activity.
Advertising planning.
The main directions of advertising research
Definition and classification of criteria for choosing advertising media.
Advertising effectiveness indicators.
Characteristics of advertising distribution channels.
Media planning, key indicators.
The process of creating an advertisement.
Approaches to developing an advertising budget
Methods of formation of the advertising budget.
The concept of advertising effectiveness.
Calculation of the economic efficiency of advertising activities
Efficiency psychological impact advertising.
Advertising activity control: concept, levels, types.
International code of advertising practice: purpose, main provisions.
Methods and directions of planning funds for advertising.
Regulation of advertising activities: concept, purpose, the legislative framework.
Federal Law "On Advertising": main provisions, tasks, scope.
Formation of the advertising budget: purpose, stages, factors.
Factors affecting the size of the budget
Classification of the effectiveness of advertising activities.
Methods for calculating the effectiveness of advertising.
Tests for self-study:
D) target audiences.
^ 2. economic basis advertising activity is:
B) level economic development production;
B) commodity market
D) the development of banking.
^ 3. The objectives of studying the discipline "Advertising" are:
B) promotion of recognition of the product and strengthening of confidence in it;
D) stimulating demand for a particular product;
D) development of ways to promote the product.
^ 4. Students studying the discipline "Advertising" should know:
^ 5. The subject of study of the discipline "Advertising" are:
A) a set of means, methods and ways of disseminating information in a certain area economic activity people in order to attract the attention of potential consumers to the object of advertising;
C) encouraging people to take a specific action by psychologically influencing the audience;
A) product attributes;
B) promotion;
C) the goals and objectives of the discipline;
A) intellectual;
B) administrative;
B) psychological;
D) emotional.
^ 9. Humanity is a trait of bona fide advertising:
A) marketing
B) the economics of industry;
B) pricing;
D) commercial activity.
^ 11. Historically the first form of mass advertising:
^ 12. Composer - participant of the advertising process:
A) a letter sent to a specific addressee with information about the company's product;
B) speech on the radio of the head of the company's product;
C) a newspaper report about the sale of the company's product.
1) adds an invisible value to the product;
2) uses rational treatment;
3) creates an image over time;
4) causes immediate action.
^ 16. Country where advertising flourished most in the 19th century:
A) Austria
B) England;
In Russia;
D) France.
17. In order to characterize a certain message as advertising, it is important to make sure that:
a) the non-personal nature of the presentation and promotion of ideas, goods or services;
B) payment for the message by a well-defined person interested in selling;
B) both;
D) if the first is combined with the second.
^ 18. In developed countries, the leading form of product promotion in recent years has become:
D) public relations system.
A) letters, postcards;
D) calendars.
^ 20. If we understand advertising as information distributed For a certain circle of people, then advertising is not allowed will call:
A) information in publications distributed only by subscription;
B) information addressed to specific segments of the consumer market;
C) information that is relevant only to certain customers;
D) information that is not available to certain categories possible clients.
^ 21. At the stage of preparing the market for sales of a new product, the task of advertising is:
A) promotion of purchases;
B) informing about points of sale;
C) formation of potential consumers;
D) stabilization of the circle of buyers.
22.^ Specify which advertising should be used at the stage of saturation of the market with the company's product:
B) a magazine
D) printing house;
D) consumer.
24. Indicate who is a direct participant in the advertising process:
B) a magazine
D) printing house;
D) consumer.
^ 25. An indicator that can be used to characterize the goals of an advertising campaign:
A) creating and maintaining a preference for a particular product
(trademark);
B) increase in sales;
C) an increase in market share.
^ 26. Set goals advertising campaigns:
A) according to the cognitive reaction of consumers;
B) according to the emotional reaction of consumers;
C) on the behavioral response of consumers.
28. There is an opinion that a brand was a kind of advertising. Your opinion:
^ 29. Please answer whether the simultaneous use of verbal and non-verbal communication channels is complex:
^ 31. Answer, is it possible without communications any forms of relations and activities:
^ 33. Is it allowed to advertise goods if their sale requires a license, but it has not been obtained: A) yes;
34. Is it a task at the stage of introducing new products to maintain the achieved level of sales:
^ 37. Is promotional advertising an integral part of prestige advertising:
A) a strategic decision
B) tactical decision.
^
39. Establish a correspondence between the forms of marketing communications and their types:
| № | Forms of Marketing Communications | Types of marketing communications |
|||
| political | commodity | corporate | social |
||
| 1 | Advertising | ||||
| 2 | Direct Marketing | ||||
| 3 | Sales Promotion | ||||
| 4 | Public communications | ||||
| 5 | Exhibitions | ||||
| 6 | Trade fairs | ||||
^ 40. Arrange the following concepts from general to particular:
B) marketing communications;
D) mass communications;
^ 41. Arrange the following concepts from general to particular and determine the hierarchy of regulations state regulation advertising activities:
A) a special agreement regulating the relationship between the client and the advertising agency;
B) Decree of the President of the Russian Federation "On the protection of consumers from unfair advertising";
G) Regulations Ministry of the Russian Federation for Antimonopoly Policy and Entrepreneurship Support.
^ 42. Set the correct sequence of advertising functions in accordance with the ZhTsT: A) stimulating;
B) explanatory;
B) introductory;
D) convincing;
D) reminiscent.
43. Mark only one of the answers that most correctly answers the question.
a) the non-personal nature of the presentation and promotion of ideas, goods or services;
B) payment for the message by a certain sponsor interested in the announcement;
C) a) and b) are correct.
D) the personal nature of the promotion of goods and services.
44. The best of the arguments presented in the advertising message of instant coffee is the statement:
A) enables quick preparation of a cup of coffee;
B) tasty, fragrant, invigorating drink;
C) a reliable assistant for working women;
D) indispensable for meaningful communication.
A) letters, postcards;
D) calendars.
46. The leading form of promotion of investment goods on the markets is:
48. What elements are included in the complex of marketing communications:
B) personal selling and PR;
49. At what stage life cycle product is the most effective use of sales promotion?
A) at the initial stage of sales;
B) sales growth phase;
C) the maturity of the product;
1. Sales promotion methods are not used for the sale of goods for industrial purposes.
2. For the sale of industrial goods, the best means of promotion is personal selling.
A) 1 and 2 are correct;
B) 1 and 2 are wrong;
C) 1 is true, 2 is false;
D) 2 true, 1 false.
A) television
B) radio;
In Internet;
D) newspapers
D) specialized magazines;
52. Which of the following properties are the advantages of advertising on television?
A) reaching large audiences;
B) the speed of bringing information to the target audience;
C) low cost per contact;
D) flexibility of arguments;
1.When the commodity organization of the sales department of the area of activity sales agents will not intersect.
2. When organizing a sales department on a territorial basis, each agent sells all the goods of the enterprise.
A) 1 and 2 are correct;
B) 1 and 2 are incorrect;
C) 1 is wrong, 2 is right;
D) 2 true, 1 false.
54. What sales promotion methods should be used to solve the following problems?
A) increase brand loyalty;
B) increase in repeated purchases of certain brands of goods;
C) an increase in trial purchases of a new product;
D) increase consumer loyalty to the store.
55. An enterprise classifies its customers into 4 groups, which are served by 24 sales agents who work 8 hours 5 days a week. Estimate the number of sales agents.
| Customer Group | Number of clients | Number of visits per month | Time spent per client |
| The most important | 100 | 4 | 60 minutes |
| Important | 200 | 3 | 45 minutes |
| Not very important | 300 | 2 | 30 minutes |
| Not at all important | 400 | 1 | 20 minutes |
56. Analyze the advantages and disadvantages of methods for evaluating the performance of sales personnel.
A) the average number of visits per day,
B) comparison with sales in the previous period;
C) comparison with the sales of other employees;
D) comparison with sales of the best worker.
1. The lower the quality of manufactured goods, the lower the cost of their promotion.
2. The main goal of promotion is to increase the awareness of products.
A) 1 and 2 are wrong;
B) 1 and 2 are correct;
C) 1 is true, 2 is false;
D) 1 is wrong, 2 is right.
58. Explain why Russian entrepreneurs most often use advertising to promote their products.
^ 7. Educational, methodological and information support of the discipline (module)
a) basic literature
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Similar Documents
Print advertising as a tool for selling goods or services. Advertising as a dialogue, its communicative effect. The influence of pictorial print advertising on the emotional component of the consumer through visual perception. Illustrated and familiar advertising.
abstract, added 11/06/2012
The methodology for two-component evaluation of the effectiveness of print advertising and the implementation of its analysis of the effectiveness of the perception of five advertising products: outdoor advertising, television, print advertising, radio and the Internet. The problem of creativity in advertising.
term paper, added 02/11/2010
Advertising in the socio-cultural space: history and modernity. Features and types of print advertising. Petersburg print advertising market. Advertising as a means of visual communication. Conditions for the effectiveness of print advertising.
term paper, added 10/27/2006
Characteristic features of print advertising, features of its creation. Factors affecting the effectiveness of the use of print advertising in commercial activities enterprises. Direct use of print advertising in the activities of the Corporation Studio "Center".
thesis, added 07/26/2008
Characteristics and types of outdoor advertising. Booklets, flyers, posters and catalogs as subspecies of printed advertising. Purpose of radio advertising. Promotional souvenirs. Types and functions of advertising on the Internet. Classification of advertising by spheres of action.
abstract, added 03/13/2009
Psychological aspects of attracting attention to advertising. Multiplicity in advertising: repetition and intensity. Dynamics, contrast and size of advertising, its emotionality. Advantages and features of television, print, radio and Internet advertising.
test, added 01/30/2011
Characteristics of print advertising in terms of an effective means of communication in business. The essence of print advertising. Features of the text content of the advertising name. The value of print advertising for the promotion of the Corporation "Center" - a leader in business.
thesis, added 03/12/2011
Graphic features of print advertising, its visual means. The specifics of the composition, graphic techniques to draw attention to advertising. Advertising products in the hair cosmetics market. Analysis of the effectiveness of print advertising company "Wella".
term paper, added 04/08/2010