Wage employees in real conditions, it exists in two forms of its organization: time-based and piecework. In the first case, the salary is formed in proportion to the hours worked. This can be an hourly rate, a weekly rate, but most often in our conditions a monthly rate is set, which is commonly called a monthly salary. When establishing a monthly salary, the duration is stipulated working week and working day.
With a piecework form of remuneration, the employee's earnings are made dependent on the quantitative indicators of the work performed through the establishment of a payment standard for each unit of output.
By the end of the 20th century, the time-based form of wages became relatively more widespread in modern economy. The reason for this is technical process, one of the features of which is the replacement of manual labor by machines. At the same time, the final result is often very difficult to determine based on specific workers servicing the machines, which excludes in principle the use of piecework payment in its pure form.
However, where the determination of the results of individual workers is possible, the piecework system works effectively. In practice, various combinations of the principles of both time-based and piece-rate forms of payment can also be applied.
When forming wages at specific enterprises on the basis of these two forms, it is possible to use various systems remuneration of labor, taking into account the economic characteristics of a particular production. There are a lot of such systems. There are, however, some of the most general principles for the formation of a particular system of remuneration. The following fundamental approaches are distinguished, which, with a certain degree of conventionality, can be defined as theoretical concepts of wage systems:
1. Taylorism.
2. The system of analytical evaluation of work.
3. Profit sharing system.
4. Fordism.
The Taylorism system is named after the American engineer Taylor, a well-known specialist scientific organization labor. In this system, the basis for setting the amount of wages is the condition for meeting fairly strict production standards set for the employee on a working day. Subject to the fulfillment of the norm, enough is paid high salary, but in case of non-compliance with the norms, tangible penalties are applied. Accordingly, overfulfillment of the norms is encouraged by bonuses. The system encourages employees to work with maximum efficiency, often by increasing the intensity of work to the detriment of health.
The system of analytical evaluation of work takes into account several different factors that affect the effectiveness of labor (including such factors as the level of qualifications, participation in rationalization work, labor discipline). Each factor is evaluated by a certain amount of credit points, and the amount of points scored affects the level of salary.
Profit sharing systems are used by entrepreneurs in such industries, where the final results depend on the accurate work of teams of teams, workshops, sections. The workers are promised bonus payments from the profits of the enterprise if the planned profit is exceeded due to the exact observance of technology, the absence of losses and defects in the production process, and saving resources.
Fordism system (on behalf of famous businessman Ford) is used in the formation of wages in conveyor production. Final result here is directly related to the speed of the conveyor. Wage rates rise if workers agree to work under conditions of some increase in the speed of the conveyor (due to increased labor intensity).
When assessing the level and dynamics of wages, it is necessary to distinguish between nominal and real wages. The nominal amount of wages in dynamics can change quite significantly due to inflation, changes in the scale of prices, and some other factors. Therefore, it is imperative to take into account the real amount of goods that can be purchased for the amount of wages. The real wage is determined by comparing the prices of a standard set of goods in the base and current periods and is always expressed relative value. For example, consider data on nominal and real wages in Russia over the past 20 years.
Table 7.1
The data presented show that during the transition to market economy the national average salary of employees in real terms decreased by more than 2 times in relation to 1985, in the 90s of the XX century. Despite the positive growth real wages after 2000, the pre-reform level was reached only after 17 years. Note, however, that the data presented here are official statistics, which do not take into account a part of the wages actually received by employees of some enterprises (wages in envelopes that are not reflected in the financial statements).
Comparing the level of wages in Russia with the wages of employees in other countries also does not inspire much optimism. In developed countries, for example, the hourly wage rate for a skilled worker is at least $15/hour, while the same indicator in Russia is $1/hour. In our usual monthly calculation average salary in England, for example, was in 2005. more than 3000 dollars, while in Russia - 200 dollars.
The main factor that determines the possible level of wages in any country is the level of productivity of social labor. According to this indicator, Russia lags behind the developed countries by about 6-7 times (but not 15 times, as in terms of wages). According to many economists, the noted disproportion between wages and the level of labor productivity has a negative impact on the pace of economic development Russia.
Any enterprise, regardless of the form of management, pays the labor of its employees unequally, as indicated in staffing, but the ratio of salaries of employees at the enterprise is fixed in tariff scale.
This is one of the methods for calculating wages at an enterprise, which is formed on the basis of local or legislative acts, it is she who determines the coefficient for multiplying the minimum wage, depending on the qualifications of a specialist and other related ones.
When forming the tariff scale, the following is taken into account:
- The intensity of the work load;
- Harmfulness and danger of production;
- Length of working time and length of service of an employee in one position;
- Branch of production, since for each type of production its own coefficients are used;
- Employee qualification;
- Features of climatic conditions.
Important: the cost of an employee's hour of work is always used as a basis in the tariff scale.
The volume of work performed by him per shift can be taken into account, while it is subsequently still broken down by the number of hours in the shift or working day. This leads to the calculation of the hourly rate of an employee in any production.
The differences between the tariff system and are discussed in this video:
Important: rates and increased salaries may not depend on categories. The tariff scale is formed according to the categories, usually 6 categories are used in its formation, such a system is used mainly for budgetary institutions.
If the enterprise is engaged in production and is quite complex, a larger number of digits up to 23 is used, but the same coefficients are applied as in the public sector.
The salary of each employee depends on the coefficients used.
Application of the tariff scale in organizations
Remuneration in production is formed in accordance with the legislation of Art. 143 - 145 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and when using tariff and qualification reference books.
Labor Code of the Russian Federation Article 143. Tariff systems wages
Tariff wage systems - wage systems based on the tariff system of differentiation of wages of workers of various categories.
The tariff system for differentiation of wages of employees of various categories includes: tariff rates, salaries (official salaries), tariff scale and tariff coefficients.
Tariff scale - a set of tariff categories of work (professions, positions), determined depending on the complexity of the work and the requirements for the qualifications of employees using tariff coefficients.
The tariff category is a value that reflects the complexity of the work and the level of qualification of the employee.
Qualification category - a value that reflects the level of professional training of an employee.
Tariffication of work - the assignment of types of labor to tariff categories or qualification categories, depending on the complexity of the work.
The complexity of the work performed is determined on the basis of their billing.
Tariffication of work and the assignment of tariff categories to employees are carried out taking into account a single tariff qualification handbook works and professions of workers, a unified qualification directory of positions of managers, specialists and employees, or taking into account professional standards. These reference books and the procedure for their application are approved in the manner established by the Government Russian Federation.
Tariff systems of wages are established by collective agreements, agreements, local regulations in accordance with labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing norms labor law. Tariff systems for remuneration of labor are established taking into account the unified tariff-qualification directory of works and professions of workers, the unified qualification directory for the positions of managers, specialists and employees or professional standards, as well as taking into account state guarantees for wages.
These directories are a list of activities and various professions that are available in enterprises and institutions. They fully contain the characteristics and qualification data, as well as the complexity of all types of professions. In addition, they indicate the requirements for the skills and experience of employees, determine their degree of responsibility.
Important: the directory is designed to determine and assign a rank to each employee.
Of course, at the enterprise, the management has the right to develop its own tariff-qualification guide, taking into account the characteristics of the organization's activities.
Important: in this case, the guarantees and rights of the employee should not be infringed, in particular, labor should not be paid below the minimum wage.
Classification according to new standards
Classification in the tariff scale occurs on the basis of several components:
- Industry;
- State and commercial organizations;
- division within the enterprise.
For example, in the pricing of payments for medical workers their categories, base salary and minimum wage are involved.
In addition, rates are based on:
- Centralized act established by the authorities;
- The contractual basis is a collective agreement.
At the same time, a new wage system is applied, but taking into account the old foundations.
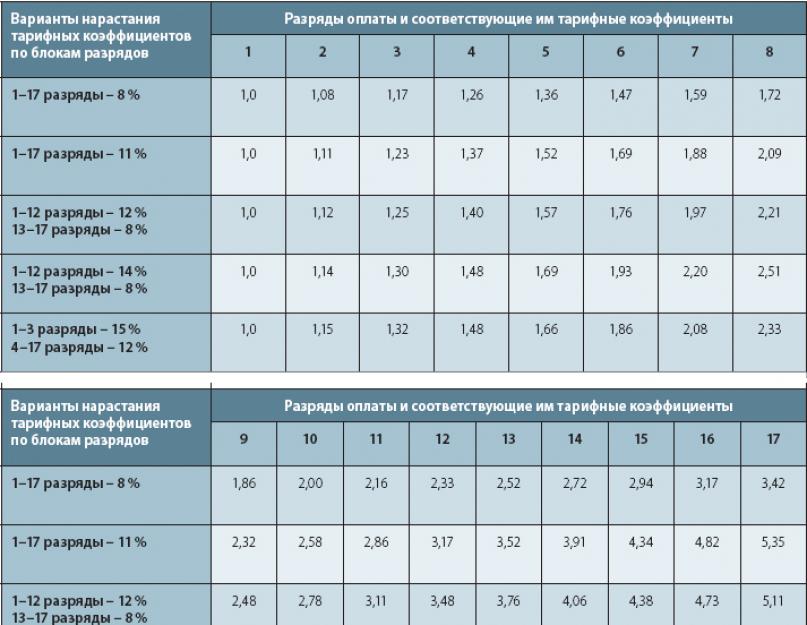
 Payment grades and coefficients.
Payment grades and coefficients. Rank Odds and Pay Rates
The coefficients used may vary depending on the industry, but for budget organizations fixed indicators are used in almost any field.
For example, for budgetary organizations in medicine, the following figures apply:
| 1 | 1 | 1 100 |
| 2 | 1,04 | 1 144 |
| 3 | 1,09 | 1 199 |
| 4 | 1,142 | 1 256,2 |
| 5 | 1,268 | 1 394,8 |
| 6 | 1,407 | 1 547,7 |
| 7 | 1,546 | 1 700,6 |
| 8 | 1,699 | 1 868,9 |
| 9 | 1,866 | 2 052,6 |
| 10 | 2,047 | 2 251,7 |
| 11 | 2,242 | 2 466,2 |
| 12 | 2,423 | 2 665,3 |
| 13 | 2,618 | 2 879,8 |
| 14 | 2,813 | 3 094,3 |
| 15 | 3,036 | 3 339,6 |
| 16 | 3,259 | 3 584,9 |
| 17 | 3,510 | 3 861 |
| 18 | 4,500 | 4 950 |
Important: at the same time, if the employee works in countryside, then 25% of the base salary is added to his salary.
If this is a deputy, then his salary is 10 - 20% lower than the head, taking into account qualifications, degrees, honorary titles.
If the specialty is not indicated in the tariff intersectoral reference book, then such a specialist is paid in accordance with the unified tariff and qualification reference book.
Examples of payment calculations
If hourly wages are used, then the number of hours worked is simply multiplied by the hourly rate.
The employee worked 150 hours per month, his rate per hour is 134 rubles, it follows that he earned:
150 * 134 = 20,100 rubles per month.
Since he fulfilled the plan, according to the collective agreement, he is entitled to a bonus of 20% of earnings, that is:
- 20,100 * 0.2 = 4,020 rubles bonus. You will find out by what rules the monthly bonus is calculated for employees.
- 20,100 + 4,020 = 24,120 rubles earnings.
In addition, he has a 5th category, and this involves the use of a coefficient of 1.268, which indicates the employee’s earnings in a given month of 30,584.16 rubles.
Important: if the employee has not fulfilled the plan, then the employer has the right to deprive him of the allowance.
Conclusion
The pay scale is a great advantage if it is used in accordance with innovations and, first of all, the value of the employee, his experience and complexity are assessed production process, and already at the next step is the rank of a managerial position.
How to build an effective wage system in an enterprise - see here:
Lekhtyanskaya Larisa Vladimirovna, candidate economic sciences, Associate Professor, Department of Management and Economics, Vladivostok State University economy and service, branch in Nakhodka, Russia
Rimskaya Tatyana Grigorievna, Candidate of Historical Sciences, Associate Professor of the Department of Civil Engineering, Director, Vladivostok State University of Economics and Service, branch in Nakhodka, Russia
A wage is a person's monetary reward for his work. It depends on the qualifications of the employee, the quality and quantity of the work performed, as well as the complexity of the work; is the price paid for the use of labor. Basically, there are two types of wages: nominal wages and real wages. Nominal wages are directly the amount of money received for labor, and real wages are the amount of goods and services that can be bought with this amount of money. (Tokarev, Kulikova, 2015). If we talk about wages, then there must be a labor market. As in any market for goods and services, there are sellers and buyers of labor in the labor market. The sellers of labor are skilled workers, and the buyers are firms that need employees, labor. In progress economic relations between sellers and buyers, the price of labor power is formed. This is wages in the form of working tariffs, salaries, piecework and time wages. (Tyugashev, Kulikova, 2015).
This is how the supply and demand for labor is formed. Demand- those people and firms that need employees, workforce (Moshkova, Kharlamova, 2011). Offer - people who offer their work for a monetary reward.
Purchase and salelabor force is carried out under an employment contract. This agreement is the main document governing labor Relations between an employer and his employees. The rights and obligations of the parties are also set out in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation dated December 30, 2001 No. 197-FZ.
Pay for laboris the remuneration that workers receive for providing their workforce. Wage rate– wages per unit of time. Therefore, the level of wages depends on the demand for labor in comparison with the supply. The demand for labor is directly related to its productivity. (Khalikova, 2011).
Labor productivity determined by the quantity and quality of products produced.
Labor supply will depend on the proportion of the working-age population. The following dependency arises: the more labor force in a certain market with a given demand, the lower the wage level (Mironova, Egorov, 2014).
Wages are formed in a particular labor market, depending on the quality of the workforce. In a competitive labor market, the equilibrium price of wages will be the sum of the intersection of two curves: supply and demand. This intersection will be the optimal point for both sides - buyers and sellers of labor (Stytsyuk, 2014).
Highlight the main features competitive market labor:
- the presence of firms that provide the same services, produce the same products, compete with each other and offer the same conditions for highly skilled workers of a certain type of labor;
- a significant number of workers who offer a certain type of work, independently of each other, and having the same qualifications;
- the wage rate in such a market cannot be dictated by anyone, and no one exercises control over it (Skulsky, 2014).
The next labor market model– monopsony. Monopsony- a situation in the market when only one buyer cooperates in the market with many sellers who dictate the price and sales volume. Monopsony is characterized by the following features:
- it is impossible for employees to find another place of work due to the characteristics of the profession, living conditions or geographical factors;
- workers of a certain type of labor are employed in one firm;
- The firm controls salary (Shalaeva, Vakhovsky, 2014).
The supply and demand curve of labor in such a market will have an uplifting appearance, all points on this graph will show the wage rate of one worker for any given number of workers employed. (Andreeva, 2006).
A significant role in developed countries is played by trade unions acting as a defender of the rights of the worker. The main economic task of trade unions is to increase the wages of workers. To do this, they use various methods to achieve the main goal (Zayarnaya, 2014).
The goal of trade unions is seeking a pay rise, the goal of employers– keep the level of wages at the achieved level, reducing costs and increasing profits.
Conclusion
1. Wages in different markets are formed differently. It depends on the balance of supply and demand in specific labor markets. There is a formation of wage rates for workers. This differentiation is determined by specific reasons:
- workers are not homogeneous, i.e. differ in abilities, level of education, training, qualifications.
- certain types of work differ in their attractiveness, working conditions, and other factors.
2. The quality of the labor force differs due to investment in human capital.
3. Trade unions are fighting to improve working conditions, to prevent injuries at work, they always oppose layoffs, even in cases where the employer is forced to optimize due to a number of existing reasons: lack of sales for products, lower prices for manufactured products. Trade unions are given the right, if it is impossible, to agree with the employer on raising the wages of employees, when there are all the necessary indicators for raising it, to go on strike, but this is an extreme measure, and in practice, agreements on wage increases are most often reached.
Moscow + 7 495 648 6241
Salary is a remuneration for work depending on the qualifications of the employee, the complexity, quantity and conditions of the work performed, as well as compensation and incentive payments.
In the socio-economic life of society, wages play an important role: as a personal income, it serves as the main material source of livelihood for workers and their families, and as an aggregate payment demand, it is one of the factors in maintaining and developing production. In a market economy, wages are influenced by a number of market and non-market factors. As a result, a certain level of wages is formed. The determining factors influencing the amount of wages are the interaction of demand for labor and its supply, as well as the level of technology, technology and organization of production, efficiency public policy in this area, the degree of influence of trade unions, etc.
Wages are an element of the employee's income, a form of economic realization of the right of ownership to the labor resource belonging to him. At the same time, for an employer who buys a labor resource to use it as one of the factors of production, the remuneration of employees is one of the elements of production costs.
The opportunity to sell your labor exists only in a market economy. A man, in order to sell his labor, must be personally free. In the traditional system, people do the same thing as their parents. In a command economy, it is up to the authorities, the government, and the state to decide who does what.
The size of supply in the labor market is equal to the size of the economically active population - the total number of people who are self-employed (including in their own enterprise) and the unemployed who are looking for work.
Factors affecting the labor supply:
Demographic (birth rate and age composition of the population)
Social (first of all, the share of working women and pensioners)
Factors that determine the magnitude of demand for labor - economic growth / recession.
The price in the labor market is the wage rate, i.e. its value for a certain unit of time.
Factors affecting the formation of wages:
State minimum wage
performance level
Skill level
Seniority
Intensity
The complexity of labor
Quality and urgency
Dynamics of prices for consumer goods and services
Features of the labor market:
Heterogeneous goods - the labor of different workers is offered different specialties in different areas (but in macroeconomics, we nevertheless consider the labor market, unemployment and employment on the scale of the entire economy as a whole).
The wage rate is less volatile than the prices of other goods. The living conditions of most citizens directly depend on the price.
But things are different for labor sellers. As a rule, labor is the only thing they can sell.
The usual market competition between sellers and buyers (the former want to sell more expensive, the latter want to buy cheaper) in the labor market reach the degree of sharp contradictions.
The conclusion of a labor contract has an important difference from the purchase of a service.
The main element of wages is the wage rate. However, it does not take into account individual differences in the abilities of workers, their physical strength and endurance, speed of reaction, diligence, etc. Therefore, a variable part is also distinguished in the wage structure, reflecting differences in individual results of labor activity (bonuses, allowances, piecework earnings ). In addition, there are different kinds income that an employee can receive due to the fact that he works in this organization (material assistance, food, travel and treatment, valuable gifts, additional medical and pension insurance). Together, wages and these types of income can be considered as the labor income of an employee of this organization.
To the main market factors that affect the wage rate include:
1. Changes in supply and demand in the market for goods and services in the production of which this labor is used. A decrease in demand in the market for goods and services leads to a reduction in output, and consequently to a drop in demand for the resource used and vice versa;
2. the usefulness of the resource for the entrepreneur (the ratio of the value marginal income from the use of the labor factor and the marginal cost of this factor). It characterizes the ratio of the marginal income from the use of the labor factor and the marginal costs for this factor;
3. elasticity of demand for labor. An increase in the price of a resource, an increase in the costs of an entrepreneur, lead to a decrease in the demand for labor, and hence the conditions of employment. At the same time, the price elasticity of demand for labor is not always the same and depends on the nature of the dynamics of marginal income, the share of resource costs in costs, and the elasticity of demand for goods;
4. interchangeability of resources. The employer's ability to reduce labor costs with the same technical base is limited. The main opportunities for reducing labor costs are associated with a reduction in the variable part of earnings, however, the conditions of collective labor agreements act as a deterrent;
5. change in prices for consumer goods and services. The rise in prices for goods and services causes an increase in the cost of living, i.e., an increase in the reproduction minimum in the structure of the wage rate.
Section 2. Formation procedure official salaries(salaries, wage rates)
2.1. Official salaries of heads of regional public institutions secondary vocational education of culture and heads of educational and methodological (methodical) centers (offices) of regional educational institutions of culture are established in accordance with the group of institutions for remuneration according to tables 1,
The procedure for classifying educational institutions of culture as wage groups is established by a separate regulatory legal act of the regional executive authority that exercises the functions and powers of the founder.
2.2. Official salaries of deputy heads, head of a branch, chief accountant, chief engineer, deputy heads of department ( structural unit), deputy chief accountant of educational institutions of culture are set at 5 percent below the official salary of the relevant head, taking into account the pay group to which the educational institution of culture is assigned, and the individual qualification category of each individual employee.
2.3. Official salaries of specialists and other employees (except for teachers) of educational institutions of culture are established taking into account the level of professional training and the availability of a qualification category assigned based on the results of certification.
2.4. Certification is carried out in relation to:
managers, specialists and other employees of cultural educational institutions - based on the requirements qualification characteristics positions of cultural workers of the Russian Federation, qualification characteristics of the positions of educational workers of the Russian Federation;
employees of industry-wide positions - based on the requirements of qualification characteristics for industry-wide positions employees;
working professions - on the basis of tariff and qualification requirements for industry-wide professions of workers.
Workers whose professions are not provided for by the tariff and qualification characteristics for industry-wide professions of workers are attested in accordance with the work and professions of workers.
The procedure for attestation of employees of educational institutions of culture, including the procedure for the formation of attestation commissions, is established by the institution independently.
In accordance with the Procedure for the Application of the Unified Qualification Directory for the Positions of Managers, Specialists and Employees, approved by the Decree of the Ministry of Labor and social development of the Russian Federation dated February 9, 2004 N 9, persons who do not have special training or the necessary work experience, but who have sufficient practical experience and performing qualitatively and in full the tasks assigned to them official duties, by recommendation attestation commission are appointed to the respective positions in the same way as persons with special training and work experience.
2.5. The wage rates of teachers of regional state institutions of secondary vocational education of culture and educational and methodological (methodological) centers (rooms) of regional educational institutions of culture are calculated by the formula:
Basic salary rate for teaching staff;
An increase in the basic wage rate in the amount of 100 rubles. - in regional state institutions of secondary vocational education of culture and educational and methodological (methodological) centers (offices) of regional educational institutions of culture (the size of the monthly monetary compensation to provide book publishing products and periodicals established as of December 31, 2012).
Basic wage rates for teachers of regional state institutions of secondary vocational education of culture and educational and methodological (methodological) centers (rooms) of regional educational institutions of culture are established taking into account the level of professional training and the availability of a qualification category of pedagogical workers.
Basic wage rates for teachers are set for persons with higher professional education, qualification category, in accordance with tables 3
For teachers who do not have a higher professional education, the basic wage rates are set lower by 5 percent.
2.6. For teaching staff, for the specifics of their work, wage rates are set at an increased rate in accordance with Appendix No. 2 to this Regulation.
Sizes of compensation and incentive payments specified employees are established taking into account the increase provided for in part one of this clause.
2.7. Concertmasters and teachers of musical disciplines who graduated from conservatories, music departments and departments of club and cultural and educational work of cultural institutions, pedagogical institutes (universities), pedagogical and music schools, working in educational institutions culture, wage rates are set as for employees with higher or secondary musical education.
2.8. Official salaries of librarians of regional state institutions of secondary vocational education of culture are established in accordance with tables 5, Appendix No. 1 to this Regulation.
2.9. Official salaries of employees of educational and auxiliary personnel of regional state institutions of secondary vocational education of culture are established in accordance with table 7 of Appendix No. 1 to this Regulation.
2.10. Official salaries of employees of regional state institutions of secondary vocational education of culture are established in accordance with table 8 of Appendix No. 1 to this Regulation.
2.11. Salaries for the professions of workers of regional state institutions of secondary vocational education of culture are set depending on the tariff categories assigned to them in accordance with the Unified Tariff and Qualification Reference Book of Works and Professions of Workers.
The salaries of workers are established in accordance with Table 9 of Appendix N 1 to this Regulation.
2.12. Workers who have the highest category according to the Unified Tariff and Qualification Directory of Works and Professions of Workers and perform the work provided for by this category, or highest complexity permanently employed in important and responsible work (highly skilled workers), increased salaries are set by the head of the institution in agreement with representative body workers in increased sizes in accordance with table 10 of Appendix N 1 to this Regulation.
These salaries are based on indefinite term or for the period of performance of a certain work.
The introduction, change or cancellation of increased salaries is carried out by the employer in compliance with the rules for changing conditions employment contract provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
2.13. Changes in the size of official salaries (salaries, wage rates) are subject to compliance with the requirements of labor legislation within the following terms:
upon receipt of education or restoration of documents on education - from the day of the order of the head on the basis of the submission of the relevant document;
when it changes qualification category- according to the date specified in the order of the head of the institution;
when assigning a qualification category - according to the date specified in the order of the executive authority or institution under which the certification commission was created.